 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeGive scientific terms for each of the following
The formation of blood cells in the bone marrow.
State the best known contribution of:
(i) Nawaschin (ii) John Otto
(iii) Went (iv) T.R. Malthu
(a) Draw a neat and fully labeled diagram of a T.S of dicotyledonous stem.
(b) List three differences between micronutrients and macronutrients of plants.
(c) Describe the significance of osmosis in plants.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Describe the cohesion and transpiration pull theory of ascent of sap.
(b) Explain the sequence of events between pollination and fertilisation in plants.
(c) State and explain Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors.
(a) Write two functions each of:
(i) Amniotic fluid (ii) Human placenta
(b) Briefly explain the procedure followed for haemodialysis.
(c) Explain the origin and conduction of heart beat in man.
a) What is reflex action? Draw neat labeled diagram of reflex arc.
(b) Mention a cause and symptom of each:
(i) Osteoporosis (ii) Constipation.
(iii) Asthma (iv) Tetany
(c) Write four functions of the human skeletal system.
(a) Explain the effects of gibberellins on plants.
(b) Describe the mechanism of pulmonary gaseous exchange.
(c) Mention the site of secretion and function of the following hormones:
(i) Choleystokinin (ii) Oxytocin
(iii) Insulin
(a) Gibberellins are chemically gibberellic acid. The effect of gibberellins on plant are :-
(i) The elongation of stem which is carried out by the increase in cell length.
(ii) Overcome the genetic dwarfism in certain plants. Such dwarfism is caused by the mutation of a single gene that is responsible for a block in metabolic pathway leading to the synthesis of gibberellins. When gibberellins are applied to dwarf plants, they elongate normally.
(iii) Breaking of dormancy when the buds of deciduous trees and evergreens growing in temperate regions usually become dormant in late summer or early fall.
(iv) Gibberellins can substitute the photoperiodic or temperature requirement for flowering in certain plants. Its application increase the number of male flowers and decreases the female flowers.
(v) Seed germination is carried by gibberellins.
(b)
Pulmonary gas exchange takes place in the lungs between the alveoli and the blood. It is also referred to as ‘external respiration’ as it involves the respiratory processes that have contact with the external environment.
The process of pulmonary gas exchange removes CO2 from the blood and replenishes the bloods O2 supply.Gas exchange occurs down a pressure gradient, by the process of diffusion.
The air that we breathe consisting of a mixture of gases including O2 and CO2.These gases each have a pressure related to their concentration within the gas mixture. These individual pressures are termed partial pressures.
Differences in the partial pressures between the gases in the alveoli and blood create a pressure gradient across the respiratory membrane (membrane separating the alveoli and blood capillaries).
If the pressure on each side of the membrane were the same there would be no exchange of gas and no movement of O2 and CO2. Where the partial pressures of O2 and CO2 are different gas exchange occurs.
Gases move from an area of high concentration (high pressure) to an area of low concentration (low pressure). As the freshly inspired air in the alveoli is high in O2, the O2 diffuses across the respiratory membrane into the blood where the concentration of O2 is low.
The pulmonary artery contains venous (deoxygenated) blood which is carried to alveolar capillaries. The blood inside Capillaries has low oxygen tension but high CO2 tension. Thus oxygen from alveolar air passes into pulmonary capillaries and CO2 from Capillaries passes into alveolar air simply by the process of diffusion. When O2 diffuses into blood in external respiration most of it enters RBC to unite with a respiratory pigment haemoglobin to form unstable compound called oxy haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is complex protein compound containing iron which has a great affinity for oxygen. Thus, oxygenated blood is transported to the body.
c)
| Hormone | Site of secretion | Function |
| Cholecyctokinin | Enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum | Responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein |
| Oxytocin | Posterior pituitary gland | Initiates muscle contraction in the uterus during childbirth |
| Insulin | 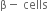 of the pancreas of the pancreas |
Lowers the sugar level of the blood |
(a) Describe the procedure of hybirdisation in plants.
(b) Name the causative agent and the main preventive measure for each of the following diseases:
(i) Amoebiasis
(ii) Rabies
(iii) Pneumonia
(c) What is manure? Explain any two types of manures.
(a) State three differences between Homologous and Analogous organs and give an example of each.
(b) Explain the resistance of mosquitoes to pesticides such as DDT
(c) What is the importance of preservation the germplasm of wild species?
