 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Give any three characters that have developed during human evolution.
(b) Explain the term chemogeny.
(c) Give any two distinctive features of Dryopithecus.
(a) Explain the evolution of giraffe’s neck according to Lamarck’s theory of evolution.
(b) Give two chromosomal similarities between man and apes.
(c) Name any two temporary embryonic structures in vertebrates which provide evidence for evolution.
(a) Persons suffering from sickle cell anaemia are at an advantage in Malaria infested areas. Explain.
(b) Define the term gene flow.
(c) What are analogous organs? Describe with one example from the plant kingdom.
(a) With the help of diagrams, name and describe the different types of placentation seen in angiosperms.
(b) Give four points of anatomical differences between a monocot stem and a dicot stem.
(c) Define the following terms:
(i) Racemose inflorescence
(ii) Osmotic pressure
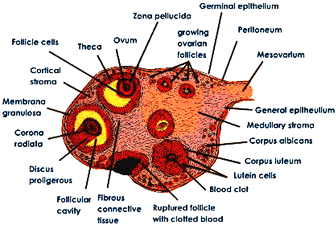
(a) Draw a diagram of the internal structure of the human ovary.
(b) Define the term water potential.What are its components? Explain.
(c) Give definition and importance of:
(i) Imbibition
(ii) Parturition
(a)
(b) Water potential  - is the difference in the free energy/kinetic energy of water molecules in the solution and that of a pure water at the same temperature and pressure. Kinetic energy per mole of water or the tendency of water to leave the system is known as the water potential.
- is the difference in the free energy/kinetic energy of water molecules in the solution and that of a pure water at the same temperature and pressure. Kinetic energy per mole of water or the tendency of water to leave the system is known as the water potential. 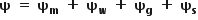
Components ;
1. Matrix potential - Symbol ψm. A component of water potential due to the adhesion of water molecules to nondissolved structures of the system, i.e. the matrix, such as plasma membranes or soil particles.
2. Solute potential - Solute potential (Ψ s) decreases with increasing solute concentration; a decrease in Ψs causes a decrease in the total water potential.
3. Pressure potential - (Ψp) In a plant cell, pressure exerted by the rigid cell wall that limits further water uptake.
(c)
(i) Imbibition is the surface absorption of water by non-living hydrophillic substances like cellulose or colloids due to surface attraction.
Imbibition is important as:
It is the very first process by which the roots absorb water.
It is important of the germination of the seeds.
(ii) Parturition is the ejection of the full grown foetus from the uterus on completion of the gestation.
It is important for the birth of the child.
(a) Give four adaptations in flowers pollinated by insects.
(b) Describe the mass flow hypothesis for translocation of organic solutes (food) in plants.
(c) Write a brief note on the causes of infertility.
(a) Give any four reasons for Mendel’s success.
(b) Briefly describe the technique employed in DNA fingerprinting.
(c) Give any two features of Genetic Code.
(a) Explain the mechanism of action of T cells to antigens.
(b)Explain how insulin can be produced using recombinant DNA technology.
(c) What is pisiculture? Give one advantage.
(a)Name the causative organism andpreventive measures for each of the following:
(i) Swine flu
(ii) Typhoid
(iii) Filariasis
(iv) Syphilis
(b)State four causes and four consequences of population growth.
(c)Differentiate between:
(i)Cannabinoids and Barbiturates
(ii)Biotic potential and Carrying capacity
