 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhen two thin lenses of focal lengths f1 and f2 are kept in contact, prove that their combined focal length 'f' is given by ![]()
An electron beam passes through crossed electric and magnetic fields of 3.4 x 104 Vm-1 and 2 x 10-3 Wb mr-2 respectively. If the path of the beam remains undeviated, calculate the speed of the electrons.
If the electric field is removed, what will be the radius of the circular path described by the electrons ?
The path is undeviated, hence,
Electric force of electron = Magnetic force on electron
eE = evB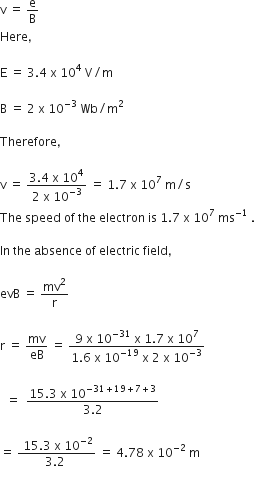
The radius of the circular path will be 4.78 x 10-2 m or 0.0478 m.
Draw the energy level diagram of a hydrogen atom; and draw arrows to show transitions responsible for:
(i) Absorption lines of Lyman series.
(ii) Emission lines of Balmer series.
In photo-electric effect, what is meant by the terms :
(i) Work function of a metal
(ii) Stopping potential.
