 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWith the help of a labelled diagram, show that fringe separation β in Young’s double slit experiment is given by:
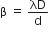
where the terms have their usual meaning.
(i) What is the difference between polarised light unpolarised light based on the direction of electric vector E?
(ii) What will be the effect on the width of the central bright fringe in the diffraction pattern of a single slit if :
(1) Monochromatic light of smaller wavelength is used.
(2) Slit is made narrower.
At what angle, a ray of light should be incident on the first face AB of a regular glass prism ABC so that the emergent ray grazes the adjacent face AC? See Figure 7 below. (Refractive Index of glass = 1.6)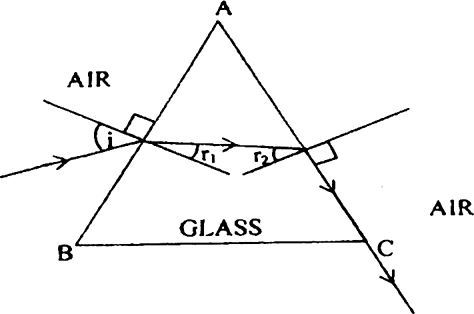
Lens makers formula: It relates focal length of a lens of the refractive index of material of lens and radii of curvature of two surfaces of lens.
Let us consider a conves lens of glass having RI n2 placed in rarer medium of Rln1. P1 and P2 be poles of C1 and C2. R1= (P1C1), R2 = (P2C2). τ= P1P2(thickness of lens).
Let a point object O be placed on principal axis at a distance is u from P1. A ray OA travelling in rarer medium is incident on first surface of lens. It is refracted towards normal at A.
If the second surface of lens were absent, the ray AB would have met the principle axis at I’ which is image of V.
Let the distance of I1 from P1 be V1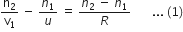
The roy AB travelling in medium n2 is actually incident an second surface of lens and refracted into rarer medium n1 bending away from normal at B. The emergent ray meets principal axis at I which is final real image of O.
For refraction at second surface I acts as vertual image and I is real image, v → distance of I from P2. 
Draw a labelled diagram of an image formed by a compound microscope, with the image at least distance of distinct vision. Write any one expression for its magnifying power.
(i) What is meant by ‘Quantization of charge?
(ii) In Thomson’s experiment, prove that the ratio of charge to the mass (e/m) of an electron is given by :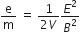
where the terms have their usual meaning.
