Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFind the minimum wavelength of the emitted X-rays, when an X-ray tube is operated at 50 kV.
i) Define half-life of a radioactive substance.
ii) Using the equation, N = No e- t, obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (
t, obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (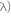 of a radioactive substance.
of a radioactive substance.
With the help of a suitable example and an equation, explain the term pair production.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time, if input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDerive an expression for intensity of electric field at a point in broadside position or on an equatorial line of an electric dipole.
Figure below shows a capacitor C, an inductor L and resistor R, connected in series to an ac supply of 220 V.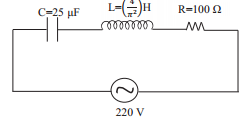
Calculate:
i) the resonant frequency of the given LCR circuit
ii) current flowing through the circuit
iii) Average power consumed by the circuit.
On the basis of Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. You must draw a labelled diagram for this deviation.