 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Typea) Two point charges Q1 = 400ô  ô and Q2 = 100ô
ô and Q2 = 100ô 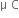 ô are kept fixed, 60 cm apart in vacuum.Find intensity of the electric field at midpoint of the line joining Q1 and Q2.
ô are kept fixed, 60 cm apart in vacuum.Find intensity of the electric field at midpoint of the line joining Q1 and Q2.
b) i) State Gauss' law.
ii) In an electric dipole, at which point is the electrical potential zero?
a) Given:
Q1 = 400ô  ô = 400 x 10-6 C
ô = 400 x 10-6 C
Q2 = 100ô  ô = 100 x 10-6 C
ô = 100 x 10-6 C
ô x = 60 cm = 60 x 10-2 m
Electric field intensity at mid-point P by charge Q1 is given by,
E1 =ô 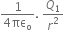
ô ô 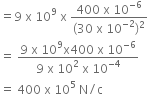 ô
ô
Electric field intensity at mid point P by charge Q2 is given by,
E2 =ô 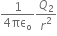
ô ô 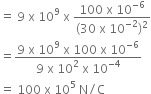
Total electric field intensity at mid point P is given by,
E = E1 - E2
ô ô = 400 x 105ô - 100 x 105
ô ô = 300 x 105 N/C
Direction of electric field intensity at mid point P is from Q1 to Q2.
b) i) Gauss Theorem states that the electric fluxô  ô through any closed surface is equal toô
ô through any closed surface is equal toô 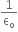 ô times the net charge q enclosed by the surface.
ô times the net charge q enclosed by the surface.
Mathematically,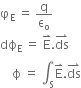
ii) At the mid point of an electric dipole electric potential is zero.
a) Obtain an expression for equivalent capacitance when three capacitors C1, C2 and C3 are connected in series.
b) A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 ohm and 0o Cand 4.8 ohm at 150o C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material?
 ô
ô a) Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to measure internal resistance of a cell. Write the working formula.
b) i) Define Curie temperature.
ii) If magnetic susceptibility of a certain magnetic material is 0.0001, find its relative permeability.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Typei) Two infinitely long current carrying conductors X and Y are kept parallel to each other, 24 cm apart in vacuum. They carry currents of 5 A and 7 A respectively, in the same direction, as shown in the figure below. Find the position os a neutral point, i.e., a point where resultant magnetic flux density is zero.
ii) If current through the conductor Y is reversedô in direction, will neutral point lie between x and Y, to the left of X or to the left of Y?
i) Define Ampere in terms of force between two current carrying conductors.
ii) What is an ideal transformer.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Typea) A coil having self-inductance of 0.7 H and resistance of 165 ohm is connected to an ac source of 275 V, 50 Hz. Ifô 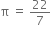 .
.
Calculate:
i) reactance of the coil
ii) impedanceô of the coil
iii) current flowing through the coil
b) Draw a labelled graph showing variation of impedance of a series LCR circuit with frequency of the a.c. supply.
a) Derive Snell's law of refraction using Huygen's wave theory.
b) Monochromatic light of wavelength 650 nm falls normally on a slit of width 1.3 x 10-4 and the resulting Fraunhofer diffraction is obtained on a screen. Find the angular width of the central maxima.
a) In Young's Double Slit experiment, show that: , where the terms have their usual meaning.
, where the terms have their usual meaning.
b) A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air-glassô pair at a polarising angle of 56o. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
