 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIf the cube roots of unity are 1, ω, ω2 then the roots of the equation (x – 1)3 + 8 = 0, are
-1 , - 1 + 2ω, - 1 - 2ω2
-1 , -1, - 1
-1 , 1 - 2ω, 1 - 2ω2
-1 , 1 - 2ω, 1 - 2ω2
If in a frequently distribution, the mean and median are 21 and 22 respectively, then its mode is approximately
22.0
20.5
25.5
25.5
Let P be the point (1, 0) and Q a point on the locus y2 = 8x. The locus of mid point of PQ is
y2 – 4x + 2 = 0
y2 + 4x + 2 = 0
x2 + 4y + 2 =
x2 + 4y + 2 =
A.
y2 – 4x + 2 = 0
P = (1, 0) Q = (h, k) such that
k2 = 8h
Let (α, β) be the midpoint of PQ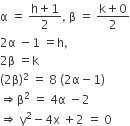
If the coefficients of rth, (r+ 1)th and (r + 2)th terms in the binomial expansion of (1 + y)m are in A.P., then m and r satisfy the equation
m2 – m(4r – 1) + 4r2 – 2 = 0
m2 – m(4r+1) + 4r2 + 2 = 0
m2 – m(4r + 1) + 4r2 – 2 = 0
m2 – m(4r + 1) + 4r2 – 2 = 0
In a triangle PQR, ∠R =π/2. If (P/2) and tan (Q/2) are the roots of ax2 +bx+ c = 0, a ≠ 0 then
a = b + c
c = a + b
b = c
b = c
The system of equations
αx + y + z = α - 1,
x + αy + z = α - 1,
x + y + αz = α - 1
has no solution, if α is
-2
either-2 or 1
not -2
not -2
The value of α for which the sum of the squares of the roots of the equation x2 – (a – 2)x – a – 1 = 0 assume the least value is
1
0
3
3
If roots of the equation x2 – bx + c = 0 be two consectutive integers, then b2 – 4c equals
– 2
3
2
2
