 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo small spheres of masses M1 and M2 are suspended by weightless insulating threads of lengths L1 and L2. The spheres carry charges Q1 and Q2 respectively. The spheres are suspended such that they are in level with one another and the threads are inclined to the vertical at angles of θ1 and θ2 as shown. Which one of the following conditions is essential, if θ1 = θ2 ?
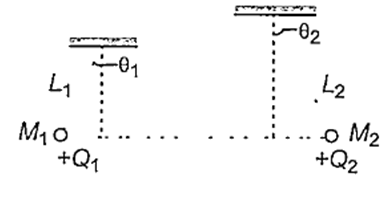
M1 ≠ M2, but Q1 = Q2
M1 = M2
Q1 = Q2
L1 = L2
B.
M1 = M2
For sphere 1, in equilibrium
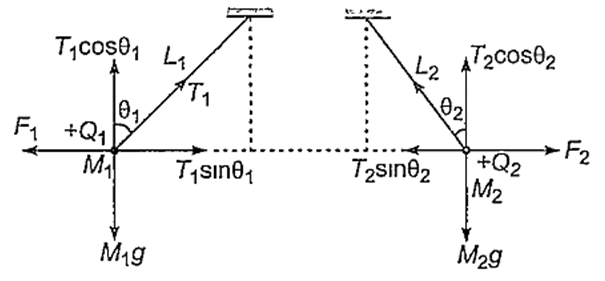
T1 cos θ1 = M1g
and T1 sin θ1 = F1
Similarly, for sphere 2,
F is same on both the charges, θ will be same only if their masses M are equal.
The moment of inertia of a circular disc of radius 2 m and mass 1 kg about an axis passing through the centre of mass but perpendicular to the plane of the disc is 2 kg m2. Its moment of inertia about an axis parallel to this axis but passing through the edge of the disc is (see the given figure).
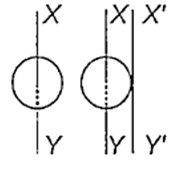
8 kg m2
4 kg m2
10 kg m2
6 kg m2
An astronaut on a strange planet finds that acceleration due to gravity is twice as that on the surface of earth. Which of the following could explain this ?
Both the mass and radius of the planet are half as that of earth
Radius of the planet is half as that of earth, but the mass is the same as that of earth
Both the mass and radius of the planet are twice as that of earth
Mass of the planet is half as that of earth, but radius is same as that of earth
The dimensions of resistance are same as those of where h is the Planck's constant, e is the charge.
A train is moving slowly on a straight track with a constant speed of 2 ms-1. A passenger in that train starts walking at a steady speed of 2 ms-1 to the back of the train in the opposite direction of the motion of the train. So to an observer standing on the platform directly in front of that passenger, the velocity of the passenger appears to be
4 ms-1
2 ms-1
2 ms-1 in the opposite direction of the train
zero
A ball rests upon a flat piece of paper on a table top. The paper is pulled horizontally but quickly towards right as shown relative to its initial position with respect to the table, the ball

Hence, the correct statement is/are
Both (1) and (2)
only (3)
only (1)
only (2)
A boy throws a cricket ball from the boundary to the wicket-keeper. If the frictional force due to air cannot be ignored, the forces acting on the ball at the position X are respected by




If the linear momentum of a body is increased by 50%, then the kinetic energy of that body increases by
100 %
125 %
225 %
25 %
A motorboat covers a given distance in 6 h moving downstream on a river. It covers the same distance in 10 h moving upstream. The time it takes to cover the same distance in still water is
9 h
7.5 h
6.5 h
8 h
Two simple harmonic motions are represented by
The ratio of their amplitudes is
1 : 1
2 : 1
1 : 3
