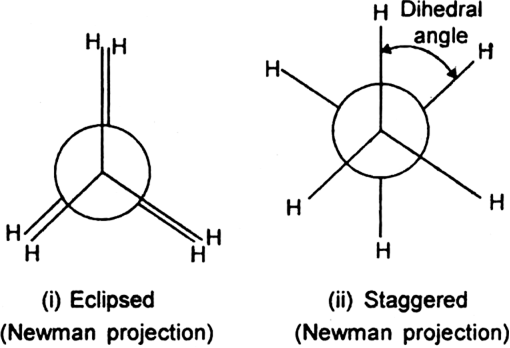
Let us fix one carbon atom and allow the other carbon atom to rotate. By doing so, we get an infinite number of arrangements (conformations) which differ in the spatial arrangements of hydrogen atoms bonded to each carbon atom. Out of these infinite number of conformations, the two are most important:
1. Eclipsed conformation (cis): In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms attached to one carbon atom completely cover or eclipse the hydrogen atoms attached to the other carbon atom in space. Consequently, the repulsion in these atoms is maximum and the conformation has maximum energy and less stable.
2. Staggered conformation (trans, anti-form): In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms are maximum apart in space and the repulsion in them is minimum. Thus, the staggered conformation has the least energy and more stable.
The eclipsed and staggered conformation of ethane are represented with the help of space
models (3D or three-dimensional separation) called saw horse models.
Newman has represented the eclipsed and staggered conformation of ethane with the help of Newman projections.