What is reforming (or aromatization)? Why is it done?
Reforming: It is a process of converting an alkane or cycloalkane with six or more carbon atoms into corresponding aromatic hydrocarbon under suitable conditions. The process which involves cyclisation and dehydrogenation is called aromatization. For example, aromatic hydrocarbons can be obtained:
(i) By catalytic dehydrogenation of cyclohexane and related compounds.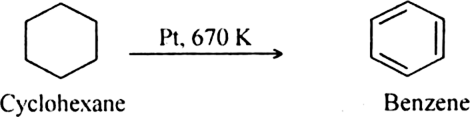
(ii) By cyclisation of alkanes (having six or more carbon atoms) to cycloalkane and then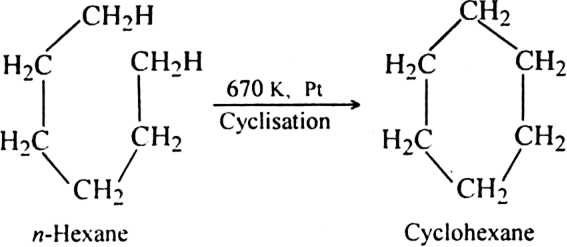
subsequent dehydrogenation at a higher temperature (≃ 670 K) in the presence of a catalyst such as platinum, palladium or nickel. For example,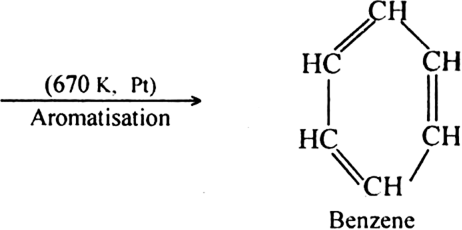
(ii) Using n-Heptane: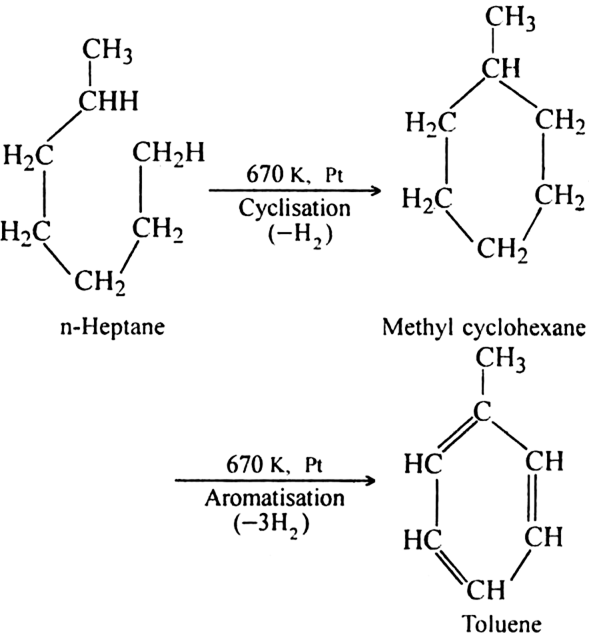
Platinum is the most suitable catalyst, therefore reforming is also called platforming.
Purpose.
(i) It is done to increase the efficiency of gasoline which acts as a fuel as aromatic hydrocarbons have been found to behave as better fuel than the corresponding aliphatic or cyclic hydrocarbons.
(ii). It is also used to prepare aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene, toluene, o-xylene etc. from alkanes and cycloalkanes.
