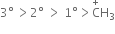What are carbocations? Discuss the relative stabilities of primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations.
 are two simple carbocations known as methyl cation and ethyl cations respectively? Carbocations are very short-lived and highly reactive species. Among primary (1°), secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) carbocations, 3° is most stable.
are two simple carbocations known as methyl cation and ethyl cations respectively? Carbocations are very short-lived and highly reactive species. Among primary (1°), secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) carbocations, 3° is most stable.
(i) Inductive effect: Alkyl groups have +I effect. In the carbocation, the alkyl group releases electrons to the positive carbon and thus reduces its charge and in turn itself becomes somewhat positive. Greater the dispersal of charge, greater will be the stability of carbocation. Thus, tertiary carbocations with three alkyl groups are more stable than secondary (with two alkyl groups) which in turn is more stable than primary (with one alkyl group). The methyl carbonium ion is least stable as it has no alkyl group.
(ii) Hyperconjugative effect. Greater the hyper conjugative structures, greater will be the stability of the ion.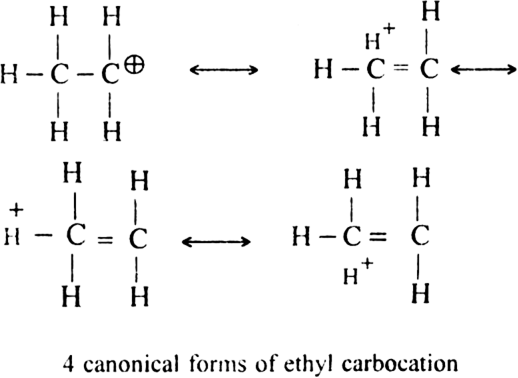
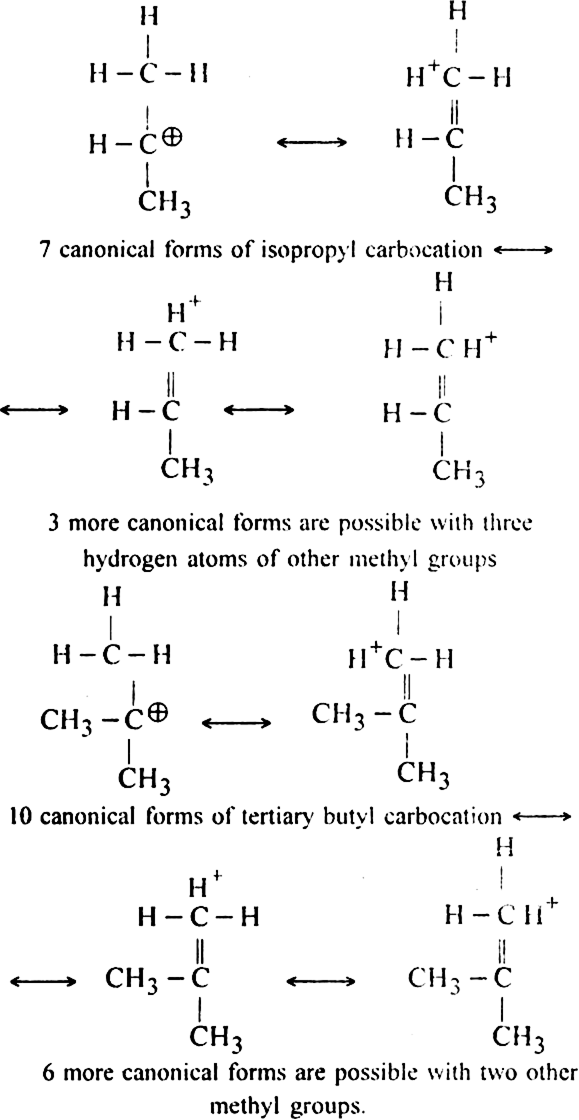
Since tertiary butyl carbocation has maximum (10) number of canonical forms, so it is most stable.
The order of stability is