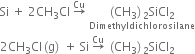What are silicones? How are these prepared? Give their uses.
Or
What are silicones? Give methods for the preparation of different types of silicones.
Silicones are polymeric organosilicon compounds containing Si – O – Si linkages. These compounds have the general formula (R2SiO). Since their empirical formula (R2SiO) is similar to that of a ketone (R2CO), they have been named as silicones. These may be linear, cyclic or crosslinked. These have very high thermal stability and are also called high-temperature polymers.
Preparation. Silicones are prepared by the hydrolysis of alkyl or aryl substituted silicon halides. Alkyl or aryl substituted silicon halides are prepared by passing gaseous alkyl or aryl halide over an alloy of copper and silicon at 300°C.
The hydrolysis of dimethyldichlorosilane gives dimethyl silanol.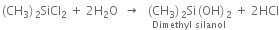
The polymerization of dimethyl silanol results in the formation of linear silicon.
Since an active OH group is present at each end of the chain, polymerization reaction continues and length of the chain increases.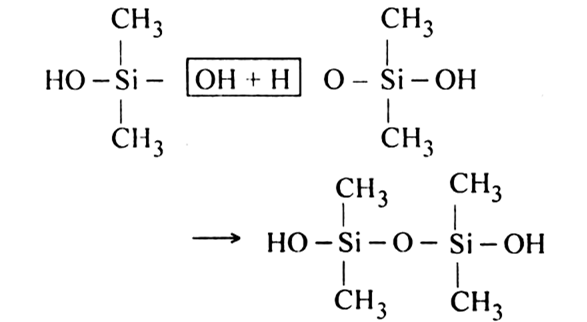
Thus, hydrolysis of a general dialkyl dichlorosilane followed by polymerization gives a linear silicon.
Crosslinked silicones. The hydrolysis of alkyl or aryl trichlorosilane gives crosslinked silicones.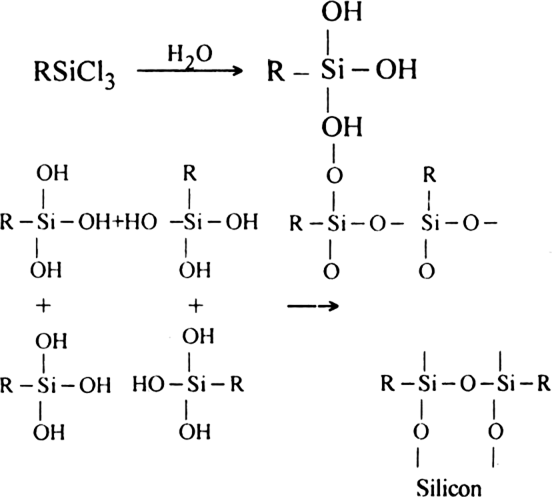
By controlled mixing of the reactants, any given type of polymer can be produced.
Cyclic silicones. Cyclic silicones may be obtained by the hydrolysis and subsequent, condensation of R2SiCl2. For example,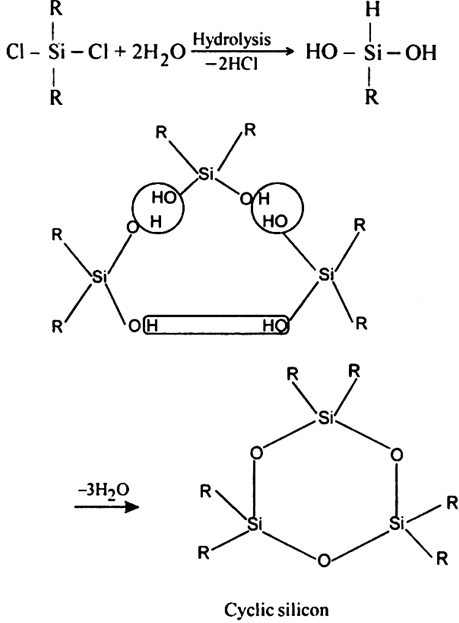
Alkyl chlorosilanes are prepared by:
(i) Grignard's reaction.
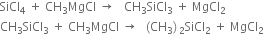
(ii) Direct process/ Rochow process.