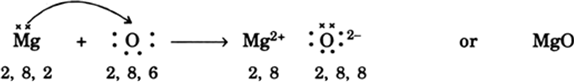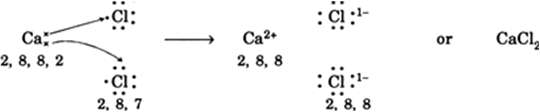Explain and illustrate using dot structures of the atoms, the formation of electrovalent bond in (i) magnesium oxide and (ii) calcium chloride.
(i) Magnesium Oxide (MgO): By entering into reaction with oxygen atom, magnesium atom (2, 8, 2) transfers two electrons to oxygen atom (2, 6). Magnesium becomes dipositive ion, Mg2+ (2, 8) and oxygen atom becomes dinegative ion, O–2 (2, 8, 8). Thus Mg2+ and O2– are held together by electrostatic forces and the formation of MgO can be shown as below:
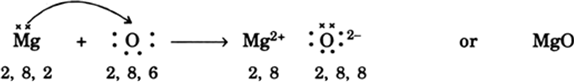
(ii) Calcium Chloride (CaCl2): In the formation of calcium chloride, two electrons from calcium atom (2, 8, 8, 2) are transferred to two chlorine atoms. Calcium atom becomes divalent positive ion, Ca2+ and chlorine atoms become monovalent negative ions, Cl–. Thus one Ca2+ ion and two CI– ions are held together as shown:
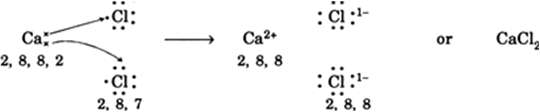
111 Views