 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAssertion: A superconductor is a perfect diamagnetic substance.
Reason: superconductor is a perfect conductor.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
B.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
A superconductor is any material that can conduct electricity with no resistance. A substance capable of becoming superconducting at sufficiently low temperatures.
Superconductor is both a perfect diamagnetic substance as well as a perfect conductor.
Which of the following subsances magnetic susceptibility χm is negative?
Diamagnetic
Paramagnetic
Ferromagnetic
antiferromagnetic
When orientation. of dipoles parallel and antiparallel to magnetic field is distributed unequally, then the material is
paramagnetic
ferromagnetic
ferrimagnetic
antiferromagnetic
Which of the following is true regarding diamagnetic substaces symbols ( symbols have their usual meaning)
μ > 1, χm > 1
μ > 1, χm < 1
μr < 1, χm < 1
μ >1, χm < 1
Assertion: The magnetic poles of earth do not coincide with the geographic poles.
Reason: The discrepancy between the orientation of a compass and true north-south direction is known as magnetic declination.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
A current I1 carrying wire AB is placed near another long wire CD carrying current I2. If wire AB is free to move, it will have
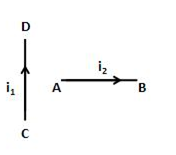
rotational motion only
translational motion only
rotational as well as translational motion
neither rotational nor translational motion
Assertion: Magnetic susceptibillity is a pure number.
Reason: The value of magnetic susceptibility for vacuum is one.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: We cannot think of magnetic field configuration with three poles.
Reason: A bar magnet does exert a torque on itself to its own field.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: The energy of charged particle moving in a uniform magnetic field does not change.
Reason: Work done by magnetic field on the charge is zero
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
