Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeState with reason any two possible consequences of elimination of decomposers
from the Earth.
Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional. Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body.
Write one difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have better chances of survival - the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Justify your answer.
What is the effect of DNA copying, which is not perfectly accurate, on the reproduction process? How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation in a combination of DNA copies of two individuals?
List three main factors responsible for the speciation and briefly describe each one of them.
A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed. Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeList two reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Name the type of bonding found in most of its compounds. Why does carbon form compounds mainly by this kind of bonding? Give a reason why the carbon compounds.
(i) Generally, have low melting and boiling points.
(ii) do not conduct electricity in the molten state.
(a) List the parts of the human eye that control the amount of light entering into it.
Explain how they perform this function.
(b) Write the function of retina in human eye.
(c) Do you know that the corneal-impairment can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of the donated eye? How and why should we organise groups to motivate the community members to donate their eyes after death?
(a) Explain the following terms related to spherical lenses:
(i) optical centre
(ii) centres of curvature
(iii) principal axis
(iv) aperture
(v) principal focus
(vi) focal length
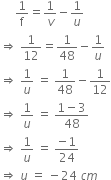
(b) A converging lens has focal length of 12 cm. Calculate at what distance the object should be placed from the lens so that it forms an image at 48 cm on the other side of the lens.