 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeName the scientist who first of all showed that an atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the black board placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. State the possible causes of this defect and explain the method of correcting it
Student is suffering from myopia defect.
Myopia or short-sightedness: Myopia is a defect in the vision, in which a person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see the distant objects distinctly after a certain limit.
This defect is common among children.
Cause of myopia: This defect arises due to either of the following two reasons:
(i) The eyeball gets elongated along its axis so that the distance between the eye lens and the retina becomes larger.
(ii) Due to excessive curvature of the cornea, the focal length of the eye lens becomes too small. 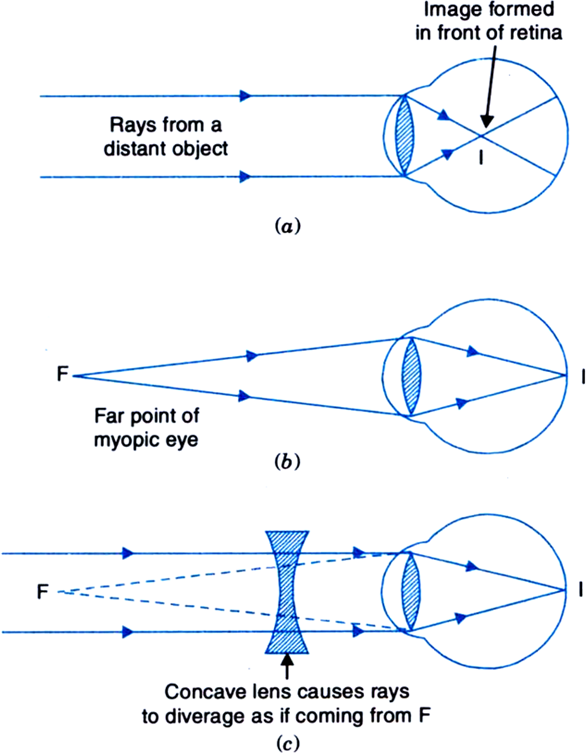
Fig. (a) and (b) Myopic eye, and (c) correction for myopia using a concave lens.
The parallel rays coming from a distant object do not meet at the retina but at a point in front of the retina because of the above causes, as shown in Fig. (a) and the distant object cannot be seen clearly.
The object has to be moved closer to the eye to a point F to focus it on the retina, as shown in Fig. (b). Thus, the far point of a myopic eye is not at infinity but only a few metres away from the eye.
Correction of Myopia: A myopic eye is corrected by using a concave lens of focal length equal to the distance of the far point F from the eye. This lens diverges the parallel rays from distant object as if they are coming from the far point F. This way, the eye lens forms a clear image at the retina.
Write the function of each of the following parts of the human eye :
(i) Cornea
(ii) Iris
(iii) Crystalline lens
(iv) Ciliary muscles
Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this phenomenon be observed by an astronaut on the Moon ? Give reason to justify your answer
Name the process by which an amoeba reproduces. Draw the various stages of its reproduction in a proper sequence
A student is viewing under a microscope a permanent slide showing various stages of asexual reproduction by budding in yeast. Draw diagrams of what he observes. (in proper sequence)
An object of height 4.0 em is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre ‘O’ of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre ‘O’ and principal focus ‘F’ on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object.
A student added few pieces of aluminium metal to two test tubes A and B containing aqueous solutions of iron sulphate and copper sulphate. In the second part of her experiment, she added iron metal to another test tubes C and D containing aqueous solutions of aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate.
In which test tube or test tubes will she observe colour change ? On the basis of this experiment, state which one is the most reactive metal and why.
