 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe chemistry of corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon. Explain the reactions occurring during the corrosion of iron in the atmosphere.
Determine the values of equilibrium constant (KC) and  G° for the following reaction:
G° for the following reaction: 
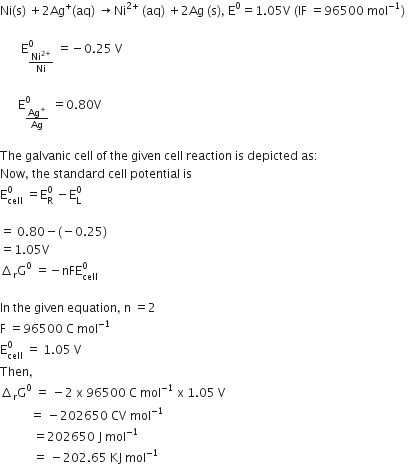
State reasons for each of the following:
The N-O bond in is shorter than the N-O bond in
State reasons for each of the following:
(i) All the P-Cl bonds in PCl5 molecule are not equivalent.
(ii) Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.
