 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain giving reasons:
(i) Transition metals and their compounds generally exhibit a paramagnetic behaviour.
(ii) The chemistry of actinoids is not as smooth as that of lanthanoids.Complete the following chemical equations:
Or
State reasons for the following:
(i) Cu (I) ion is not stable in an aqueous solution.
(ii) Unlike Cr3+, Mn2+, Fe3+ and the subsequent other M2+ ions of the 3d series of elements, the 4d and the 5d series metals generally do not form stable cationic species.
A solution prepared by dissolving 8.95 mg of a gene fragment in 35.0 mL of water has an osmotic pressure of 0.335 torr at 25°C.
Assuming that the gene fragment is a non-electrolyte, calculate its molar mass.
Classify colloids where the dispersion medium is water. State their characteristics and write an example of each of these classes.
OR
Explain what is observed when
(i) An electric current is passed through a sol
(ii) A beam of light is passed through a sol
(iii) An electrolyte (say NaCl) is added to ferric hydroxide solHow would you account for the following?
(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound but NCl3 is not.
(ii) The acidic strength of compounds increases in the order:
PH3 < H2S < HCl
(iii) SF6 is kinetically inert.Write the state of hybridization, the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complex entities:
(i) [Cr (NH3)4 Cl2] Cl
(ii) [Co (en) 3] Cl3
(iii) K2 [Ni (CN) 4]Give a chemical test to distinguish between ethylamine and aniline.
Ethylamine and aniline can be distinguished from each other by the azo-dye test.
A dye is obtained when aniline (an aromatic amine) reacts with HNO2 (NaNO2 + dil.HCl) at 0-5°C, followed by a reaction with the alkaline solution of 2-naphthol.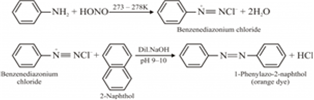
Ethylamine (an aliphatic amine) gives a brisk effervescence due (to the evolution of N2 gas) under similar conditions.
