 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer - Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson’s ether synthesis
What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
Shanti, a domestic helper of Mrs. Anuradha, fainted while mopping the floor. Mrs. Anuradha immediately took her to the nearby hospital where she was diagnosed to be severely ‘anaemic’. The doctor prescribed an iron rich diet and multivitamins supplement to her. Mrs. Anuradha supported her financially to get the medicines. After a month, Shanti was diagnosed to be normal.
(i) What values are displayed by Mrs. Anuradha?
(ii) Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes ‘pernicious anaemia’.
(iii) Give an example of a water soluble vitamin.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Ethyl iodide undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide.
(ii) (±) 2-Butanol is optically inactive.
(iii) C -X bond length in halo benzene is smaller than C -X bond length in CH3- X.
(i) Ethyl iodide undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide because in the periodic table size increase if we move down. With an increase in size, basicity decrease, and the ability of the leaving group to leave increase. Iodine is good leaving the group thus it undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide.
(ii) Optically active compounds are those which rotates plane polarised light either left or right direction. In the case of (±) 2-Butanol is optically inactive because it is both dextrorotatory i.e. (+) and laevorotatory i.e. (-) and hence forms a racemic mixture in which the net rotation of plane-polarized light towards the right is cancelled by the left one and so it becomes optically inactive.
(iii) C—X bond length in halobenzene is lower than C—X bond length in CH3—X because in halo- benzene the C—X acquires partial double bond character due to resonance as shown below whereas in CH3—X there is no such resonance. As the bond length of the double bond is smaller than single bond hence C—X bond length in halo- benzene is smaller.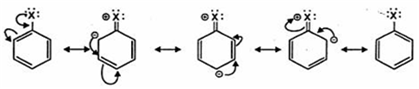
(i) What class of drug is Ranitidine?
(ii) If water contains dissolved Ca2+ ions, out of soaps and synthetic detergents, which will you use for cleaning clothes?
(iii) Which of the following is an antiseptic?
0.2% phenol, 1% phenol
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) State Raoult’s law for a solution containing volatile components.
How does Raoult’s law become a special case of Henry’s law?
(b) 1·00 g of a non-electrolyte solute dissolved in 50 g of benzene lowered the freezing point of benzene by 0·40 K. Find the molar mass of the solute. (Kf for benzene = 5·12 K kg mol-1)
