 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeGive reasons for the following:
(i) N2 is less reactive at room temperature.
(ii) H2Te is the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 16 elements.
(iii) Helium is used in diving apparatus as a diluent for oxygen.
(a) Write the hybridization and shape of the following complexes:
(i) [CoF6]3–
(ii) [Ni (CN)4]2–
(Atomic number: Co = 27, Ni = 28)
(b) Out of NH3 and CO, which ligand forms a more stable complex with a transition metal and why?
Calculate the freezing point of the solution when 31 g of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) is dissolved in 500 g of water. (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
The freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K. On dissolving ethylene glycol, freezing point, being a colligative property, will be lowered.
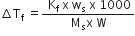
We are given that
Kf for water =1.86 K kg mol-1
Mass of solute, ws = 37 g
Molar mass of solute, Ms = 12 x 2 + 1 x 6 + 16 x 2
= 62 g mol-1
Mass of water, W = 500 g
Therefore 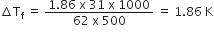
Hence, the freezing point of the solution, Tf = 273.15K – 1.86 K
= 271.29 K
Define the following terms:
(i) Primitive unit cells
(ii) Schottky defect
(iii) Ferromagnetism
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 — 10-2 to 4 — 10-2when the temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Define the following terms:
(i) Brownian movement
(ii) Peptization
(iii) Multimolecular colloids
The conductivity of 0.20 mol L-1 solution of KCl is 2.48 x 10-2 S cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (K+) = 73.56 S cm2 mol-1 and (Cl-)= 76.5 S
(b) What type of battery is mercury cell? Why is it more advantageous than dry cell?
