 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat type of magnetism is shown by a substance if magnetic moments of domains are arranged in same direction?
On adding NaOH to ammonium sulphate, a colourless gas with pungent odour is evolved, which forms a blue-coloured complex with Cu2+ ion. Identify the gas.
When a co-ordination compound CrCl3.6H2O is mixed with AgNO3, 2 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write
(i)Structural formula of the complex.
(ii)IUPAC name of the complex.
From the given cells:
Lead storage cell, Mercury cell, Fuel cell and Dry cell Ans the following:
(i) Which cell is used in hearing aids?
(ii) Which cell was used in Apollo Space Programme?
(iii)Which cell is used in automobiles and inverters?
(iv)Which cell does not have long life?
When chromite ore FeCr2O4 is fused with NaOH in presence of air, a yellow-coloured compound (A) is obtained, which on acidification with dilute sulphuric acid gives a compound (B). Compound (B) on reaction with KCl forms an orange coloured crystalline compound (C).
(i)Write the formulae of the compounds (A), (B) and C.
(ii)Write one use of compound (C).
OR
For a reaction :
(i)Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii)Write the unit of k.
The rate constant for the first-order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation: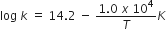
Calculate Ea for this reaction and rate constant k if its half-life period be 200 minutes. (Given: R = 8.314 JK–1mol–1).
(i) Differentiate between adsorbtion and absorption.
(ii)Out of MgCl2 and AlCl3, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged sol and why?
(iii)Out of sulphur sol and proteins, which one form multimolecular colloids?
(i) Adsorption is a surface phenomenon that causes the accumulation of molecules of a substance at the surface of a solid or liquid rather than in the bulk. In adsorption, the substance gets concentrated at the surface only. It does not penetrate through the surface to the bulk of the solid or liquid. For example, when a chalk stick is dipped into an ink solution, only its surface becomes coloured.
On the other hand, the process of absorption is a bulk phenomenon. In absorption, the absorbed substance gets uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of the solid or liquid. For example, when a sponge is dipped in water the whole sponge gets wets.
(ii)According to the Schulze-Hardy rule, the effectiveness of the salt causing flocculation depends on the charge on the ion of opposite sign to the charge on the sol particles. The greater the magnitude of the opposite charge, the higher the ability of a salt to coagulate the sol.
Thus, trivalent salt AlCl3 is more effective in causing the coagulation of a negatively charged sol than divalent salt MgCl2.
(iii)Out of sulphur sol and proteins, sulphur sol forms multimolecular colloids. Sulphur sol consists of particles containing a thousand or more S8 molecules. On the other hand, proteins form macromolecular colloids.
An element crystallizes in a f.c.c. lattice with cell edge of 250 pm. Calculate the density if 300 g of this element contain 2 × 1024 atoms.
