 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(i) An a.c. source of voltage V = Vo sin ωt is connected to a series combination of L, C and R. Use the phasor diagram to obtain an expression for impedance of a circuit and the phase angle between voltage and current. Find the condition when current will be in phase with the voltage. What is the circuit in this condition called?
ii) In a series LR circuit, XL = R and the power factor of the circuit is P1. When capacitor with capacitance C, such that XL = XC is put in series, the power factor becomes P2. Calculate P1 / P2.
Voltage of the source is given by,
V = Vo sin ωt
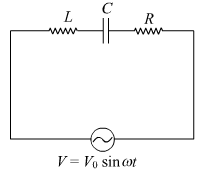
Let current of the source be I = Io sin ωt
Maximum voltage across R is VR = Vo R, represented along OX
Maximum voltage across L = VL = IO XL, represented along OY and is 90o ahead of Io.
Maximum voltage across C = VC = Io XC, represented along OC and is lagging behind Io by 90o
Hence, reactive voltage is VL - VC, represented by OB'
the vector sum of VR, VL and VC is resultant of OA and OB', represented along OK.
OK = Vo = ![]()
i.e., Vo = ![]()
![]()
Impedance, Z = ![]()
When, XL = XC , the voltage and current are in the same phase.
In such a situation, the circuit is known as non-inductive circuit.
ii)
Given,
Power factor, P1 = R/Z
Thus, ![]()
(i) Write the function of a transformer. State its principle of working with the help of a diagram. Mention various energy losses in this device.
(ii) The primary coil of an ideal step-up transformer has 100 turns and the transformation ratio is also 100. The input voltage and power are 220 V and 1100 W, respectively. Calculate the:
a) number of turns in secondary
b) current in primary
c) voltage across secondary
d) current in secondary
e) power in secondary
(i) Define the term drift velocity.
(ii) On the basis of electron drift, derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms of number density of free electrons and relaxation time. On what factors does resistivity of a conductor depend?
(iii) Why alloys like constantan and manganin are used for making standard resistors?


