 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsInstructive and permissive interactions are two major modes of inductive interaction during development. The following compares some properties of cell lines and cord blood stem cells. Cell lines, which are stored in liquid nitrogen, can be retrieved for experiments, where they behave as per their original self. Cord blood can also be retrieved from liquid nitrogen for procuring stem cells. Unlike cell lines, the stem cells can be additionally induced to undergo differentiation into desired lineages, which are very different from their original self. The behaviour of cell lines and stem cells is analogous to which of the interactions?
Both cell lines and stem cells show instructive interaction.
Cell lines show instructive interaction whereas stem cells show permissive interaction.
Cell lines show permissive interaction whereas stem cells show instructive interaction.
Both types of cells show permissive instruction.
C.
Cell lines show permissive interaction whereas stem cells show instructive interaction.
The behavior of cell lines and stem cells is analogous to cell lines show permissive interaction whereas stem cells show instructive interaction.
There are various subclasses of antibodies found in body fluids and body secretions. Many different functions ma be attributed to these subclasses. Given below in column I is major functions of different subclasses and column II consists of the name of the subclass.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Binds to macrophages by Fc. | i. IgA |
| B. Binds to mast cells and basophils. | ii. IgD |
| C. First B cell receptor. | iii. IgE |
| D. No major specific function known, other than antigen binding. | iv. IgG |
| E. Protector of mucous membrane. | v. IgM |
Select the correct combination:
A - (i); B - (ii); C - (iii); D - (iv); E - (v)
A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (iv); D - (v); E - (i)
A - (iii); B - (iv); C - (v); D - (i); E - (ii)
A - (iv); B - (iii); C - (v); D - (ii); E - (i)
The relation between cellular immune response generated against the hepatitis C virus is the critical determinant of the outcome of infection. Given below are the representative figures of the cellular immune response in column I and various outcome of infection in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
A. 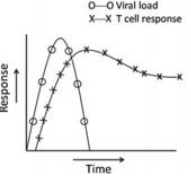 |
i. Acute |
B. 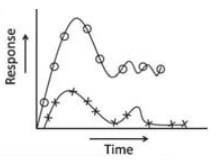 |
ii. Resolution |
C. 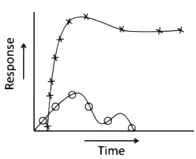 |
iii. Chronic |
Choose the best possible combination
A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (i)
A - (i); B - (iii); C - (ii)
A - (iii); B - (ii); C - (i)
A - (i); B - (ii); C - (iii)
Cellular level of tumour suppressor protein p53 is maintained by the ubiquitin ligase protein, Mdm2. Over expression of Mdm2 was found to convert a normal cell into cancer cells by destabilizing p53. Another protein 19ARF inhibits the activity of Mdm2 thus stabilizing p53. Loss of p19ARF function also converts normal cells into cancer cells. Based on the above information, which one of the following statements is correct?
Both MDM2 and 19ARF are oncogenes.
Both MDM2 and 19ARF are tumour suppressor genes.
MDM2 is an oncogene but 19ARF is a tumour suppressor gene.
19ARF is an oncogene but MDM2 is a tumor suppressor gene.
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) consist of three protein subunits α, β, and γ. In unstimulated state, α subunit is GDP bound and GPCR is inactive. When GPCR gets activated, it like guanine nucleotide exchange (GEF) factor and induces α-subunit to release its bound GDP allowing GTP to bind in its place. In order to regulate G-protein activity by regulating GDP/ GTP concentration, α subunit acts as
GTPase
GDP kinase
cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase
cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase
Physical attachment between cells is very important in imparting strength in tissues. Various physical cell junctions in vertebrate epithelial tissues are classified according to their primary functions. Enlisted below in column A is the major function of a particular junction and column B enlists cell junctions, but not in the same order.
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Seals gap between epithelial cells. | i. Desmosomes |
| B. Connects acting filament bundle in one cell with that in the next cell. | ii. Hemidesmosomes |
| C. Connects intermediate filaments in one cell to those in the next cell. | iii. Tight junction |
| D. Anchors intermediate filaments in a cell to extracellular matrix. | iv. Adherens junction |
Choose the correct combination.
A - (i); B - (ii); C - (iii); D - (iv)
A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (iv); D - (i)
A - (iii); B - (iv); C - (i); D - (ii)
A - (iv); B - (i); C - (ii); D - (iii)
Which one of the following statements about the nuclear receptor superfamily is NOT true?
The receptors are always cytosolic, where they remain associated with heat-shock proteins and have variable ligand-binding domains in the N-terminal region.
The receptors have characteristic repeat of the C4 zinc-finger motif.
The receptors are either homodimeric or heterodimeric, and in the absence of their hormone ligand, the heterodimeric receptors repress transcription, when bound to their response elements.
The receptors have a unique N-terminal region of variable length and may contain a nuclear localization signal between the DNA- and ligand0binding domains.
A protein has 4 equally spaced trypsin sensitive sites which results in peptide fragments A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5 upon digestion with trypsin. The peptides A2 and A5 represent N-terminal and C-terminal fragments respectively. Now you are asked to synthesize this protein. At time t = 0 you added all the 20 amino acids labelled with 14C and initiated the synthesis. At time t = 4, full-length protein is synthesized. If you stop the synthesis of the protein in time t = 1 and digest the protein with trypsin, which peptide will have maximum 14C label than others?
A3
A1
A4
A2
A hypothetical operon involved in the synthesis of an amino acid 'X' is 'ON' (transcribing) in the presence of low level of 'X' and 'OFF' (not transcribing) in presence of high level of 'X'. The symbols a, b, and c (in the table below) represents a structural gene for the synthesis of X (X-synthase), the operator region and gene encoding the repressor-but not necessarily in the order. From the following data, in which superscripts denote wild type or defective genotype, identify which are the genes for X-synthase, operator region and the repressor.
| Strain | Genotype | X-synthase activity in the presence of low level of 'X' | X-synthase activity in the presence of high level of 'X' |
| 1. | a-b+c+ | Detected | Detected |
| 2. | a+b+c- | Detected | Detected |
| 3. | a+b-c- | Not detected | Not detected |
| 4. | a+b+c+/ a-b-c- | Detected | Not detected |
| 5. | a+b+c-/ a-b-c+ | Detected | Not detected |
| 6. | a-b+c+/ a+b-c- | Detected | Detected |
The respective genes for 'X' synthase, the operator region and repressor are
a, b, c
c, a, b
b, c, a
b, a, c
In prokaryotes, the initiator tRNA is first charged with a methionine, followed by the addition of a formyl group to the methionine by the enzyme Met-tRNA transformylase. Given below are several statements in this context.
A. All prokaryotic proteins have formyl methionine at their amino-terminal end.
B. Deformylase removes the formyl group from the amino-terminal methionine.
C. All prokaryotic proteins have methionine at their amino-terminal end.
D. Aminopeptidases often remove the amino-terminal methionine.
E. Aminopeptidases remove amino-terminal formyl methionine.
Which of the above statement(s) are most likely to be true?
A only
B and C
E only
B and D
