 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Describe the structure of arteries, veins and capillaries. Explain the way in which each of these is adapted for its function.
(b) Give an account of the ‘Mass Flow Hypothesis’ for translocation of solutes.
(c) Give the meaning of the following:
(i) Digestion (ii) Assimilation
(a) Give a schematic representation of non-cyclic photophosphorylation showing both the photosystem.
(b) Describe the structure of a myofibril of a striated muscle.
(c) Give four points to show the importance of vegetative propagation.
(a) Describe the mechanism of inspiration and expiration in man.
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of the vertical section of the human eye.
(c) (i) What is Ageing?
(ii) Give two functions of the amniotic fluid.
(a)
(i) Draw a labelled diagram of chloroplast as seen under an electron microscope.
(ii) Name the three major photosynthetic pigments.
(b) Describe the events that take place between pollination and fertilisation in plant.
(c) Name the hormones associated with the following :
(i) The only gaseous plant regulator.
(ii) A growth inhibitor in plants.
(iii) Resorption of water from the urine in the distil convoluted tubule.
(iv) Rise in blood calcium.
(a)
(i) 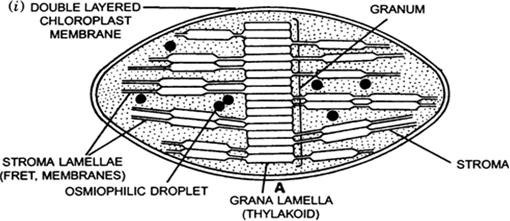
(ii) Major Photosynthetic Pigments :
Chlorophyll, Carotenoids and Phycobilins are major photosynthetic pigments found in different plants.
(b) Events taking place between Pollination and Fertilisation:
1. After reaching the suitable stigma, the pollen grains germinate and two-celled pollen grain becomes three-celled. Then it forms a pollen tube.
2. The pollen tube containing a tube nucleus and a generative nucleus grows down the walls of style. The growth of pollen tube is stimulated by a sugary substance secreted by the stigma.
3. The generative nucleus divides to form two male gametes whereas the tube nucleus disintegrates.
4. The pollen tube reaches ovary and finally turns towards the micropyle of the ovule. Then it passes through the micropyle and enters the embryo-sac. Sometimes, the pollen tube enters the embryo sac through the chalaza of the ovule.
5. After the pollen tube enters the embryo sac its tip dissolves and the male gametes are set free.
6. Out of two male gametes, one fuses with the egg cell whereas the other fuses with the secondary nucleus which is a product of the fusion of two polar nuclei.
7. This results in the fertilisation, since there are two fertilisation events it is known as Double fertilisation.
(c)
(i) Ethylene - only gaseous plant regulator
(ii) Abscisic acid - growth inhibitor.
(iii) Vasopressin (Antidiuretic hormone) - Resorption of water from the urine in the distil convoluted tubule.
(iv) Calcitonin - results in the rise in the blood calcium.
(a) Explain the DDT resistance of mosquitoes to the pesticide.
(b) What are the symptoms of Diabetes mellitus?
(c) Define :
(i) Gene pool
(ii) Genetic Erosion.
(a) Write short notes on:
(i) DNA finger printing
(ii) Cryopreservation
(iii) Hemophilia
(iv) Green manure.
(b) What are the activities of Community Health Services.
(c) Give the differences between B cells and T cells.
(a) Describe Lederberg’s Replica Plating experiment to show the genetic basis of adaptation.
(b) Give an account of chromosomal aberrations (mutations).
(c) What is a pacemaker?