Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWho was the originator of the theory of Natural Selection ? Explain the evolution of species by this theory.
Write the causative agent and the most important symptom of each of the following diseases :
(i) Whooping cough
(ii) Tuberculosis
(iii) Measles
(iv) Malaria
Differentiate between :
(i) Spontaneous and Induced Mutation.
(ii) Geographical and Reproductive Isolation.
 Long Answer Type
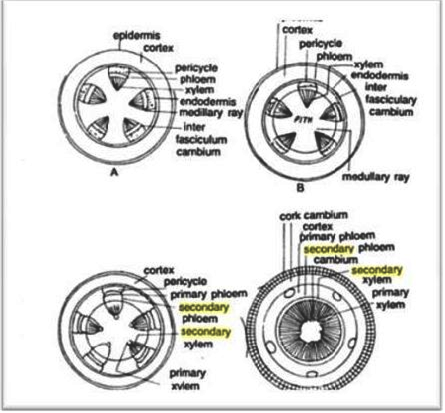
Long Answer TypeGive an account of the activity of the cambium in the secondary growth of the stem.
Secondary growth in stem—Activity of the Cambium :
1. Formation of Cambium ring : During secondary growth, the cells of medullary rays with the intrafascicular cambium develop meristematic activity and form strips of cambium called interfascicular cambium. The intra and interfascicular cambium unite to form a complete ring called cambial ring or phellogen. The activity of cambial ring gives rise to secondary growth.
2. Formation of secondary tissues : The cambial ring becomes active as a whole and starts cutting off new cells. The cells cut off on the outer side get differentiated into phloem and are called secondary phloem. The cells cut off on the inner side are modified into the elements of xylem which constitute secondary xylem. The secondary phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma. Secondary xylem consists of pitted vessels, tracheids, xylem fibres, xylem parenchyma.
3. Secondary medullary rays : Certain cells of cambium form some narrow bands of living parenchyma cells passing through secondary xylem and secondary phloem and are called secondary medullary rays. These provide radial conduction of food from the phloem and water, mineral salts from xylem.
4.Annual rings : Activity of cambium is not uniform in those plants which grows in the regions where favourable climatic conditions (spring or rainy season) alternate regularly with unfavourable climatic conditions (cold winter or dry hot summer). In temperate climates, cambium becomes more active in spring and forms greater number of vessels with wider cavities, while in winter it becomes less active and forms narrower and smaller vessels. The wood formed in the spring is called spring wood and that formed in dry summer or cold winter, autumn wood. These two woods appear together in the form of a concentric ring, in the transverse section of the trunk and this is known as annual ring. The growth of successive years appears in the form of concentric or annual rings, each annual ring representing the year’s growth.