 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(i) Give the Clifford representation of constitution of bleaching powder.
(ii) Write the chemical reactions when bleaching powder reacts with dilute HCl.
(iii) What is responsible for its oxidizing as well as bleaching properties.
Complete the following reactions and name the type of reaction to which each belongs:
i) CH3Br KOH (aq) --->
ii) H2C=CH2 +HCl --->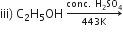
(a) Write chemical equations for the following reactions and name the main product:
(i) Formaldehyde with ammonia
(ii) Acetone with sodium hypoiodite
(iii) Oxalic acid with glycerol at 260°C.
(iv) Acetic anhydride with salicylic acid.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ on analysis was found to contain C, 79.14% and H, 5.66%. When ‘A’ is treated with alkali it does not turn brown or become polymerized but reacts as follows :
2A + NaOH = X + Y
(b)In excess of dil HCl, bleaching powder liberates Cl2.
CaOCl2 +2HCl --> CaCl2 +H2O +Cl2
Where X = A + 2H; Y gives an acid, Z, on the addition of dilute HCl; here Z is Z = A + (O). Identify the compound ‘A’ and name the reaction it is undergoing by giving reasons in support of it.
Amphoteric Nature of Glycine : In aqueous solution, glycine exists as an inner salt or a dipolar ion.![]()
This doubly charged ion is known as a Zwitter ion or an ampholyte. Due to formation of the ampholyte, glycine acts both as an acid or a base.
In aqueous solution, Zwitter ion tends to lose a proton. Hence, if electrolyzed, the negative glycine ion will migrate to anode.![]()
The pH value for the isoelectric point of glycine is 6.0.
What are the reaction products of the following ? 
(ii) Why are same compounds not obtained at the final stage ?
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Acetaldehyde and vinyl alcohol
(ii) Maleic acid and fumaric acid.
