 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA potential difference of V volt is applied across a copper wire of length I and diameter d. How will the drift velocity be affected if
(i) V is double (ii) I is doubled.

(i) just when the switch S is closed.
(ii) when sufficient time has elapsed after closing the switch.
Microwaves, X-rays, U.V. rays, infrared rays.
Which of the above electromagnetic waves has—
(i) the shortest wavelength.
(ii) the lowest frequency.
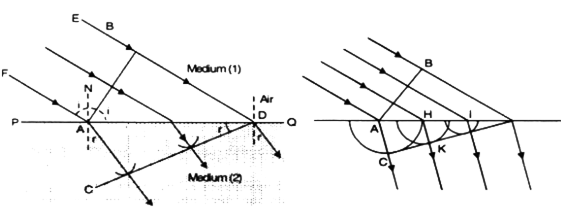
The angle between the incident ray FA and the normal NA at the point of incidence A is equal to i.
The angle is also equal to the angle between the incident plane wavefront BA and the surface of separation PQ.
So ∠BAD is the angle of incidence of the incident plane wavefront AB.
Similarly, the angle between the refracted wavefront and the surface of separation PQ is equal to the angle of refraction r.
i.e.. ∠ADC = r.
Consider the triangles BAD and ACD figure above.
sin i = 

This constant is called the refractive index of the second medium (2) with respect to the first medium (1). 
This equation proves the Snell's law.
Let the first medium be vacuum or free space of n1 = 1 and velocity of light C1 - C.
Let the refractive index of the second medium n2 be n and C2 = v.
Then, 
In a single slit diffraction pattern how does the angular width of central maximum change, when
(i) the slit width is increased.
(ii) light of smaller wavelength is used.
