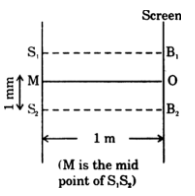
Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type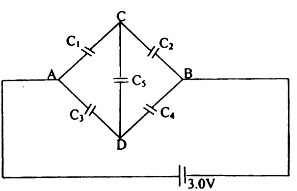
Huygen’s principle provides a geometrical method to determine the position of the wavefront at a later time from its given position at any instant.
It states that:
(1) Each point on a wavefront behaves as a new source of secondary wavelets, which spreads out in all the directions with the speed of light in the medium .
(2) The new position of the wavefront at any instant is given by the surface of tangents to the secondary wavelets in the forward direction. To explain the phenomenon of refraction by Huygen’s principle, let us consider the surface XY separating the media 1 and 2 of refractive indices μ2 and μ2, respectively and c1 and c2 be the velocities of light in the two media.
The second medium being more denser than the first and so c1 will be greater than c2 i.e., c1 > c2.
APB is the plane incident wave front. Let t be the time taken by the waves to travel the distance BC, the BC = c1t and AD = c2t. With A as centre and radius AD, draw a sphere and a tangent CD to the sphere from the point C. Then represents the refracted plane wave front.
CD is the common wave front since in the time the disturbance travels from B to C or from A to D, the disturbance at P reaches L. With point M as centre, draw a sphere such that CD happens to be tangent to the sphere.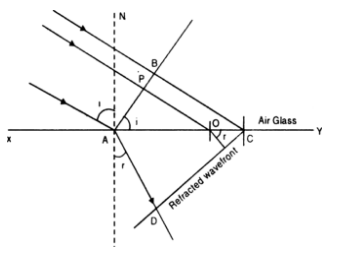
From the As ACD and MCL, we have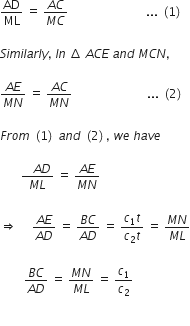
Hence, AD is the radius for secondary wave front for the point A, then ML is the radius of the secondary wave front for the point M. Let i and r be the angle of incidence and refraction, respectively. From the Δs ABC and ACD.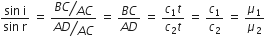
where μ2 is the refractive-index of the second medium with respect to the first medium. The above relation is Snell’s law.