 Short Answer Type
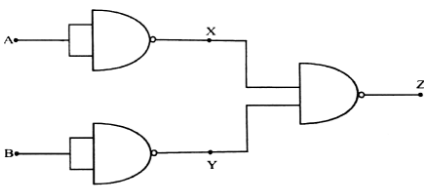
Short Answer TypeA sinusoidal voltage e = e0 Sin (wt) is fed to a common emitter amplifier. Draw neatly labelled diagrams to show:
(i) Signal voltage
(ii) Output voltage of the amplifier.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeChromatic Aberration: When white light is passed through a prism it splits up into seven colours, with violet deviated towards the base of the prism, with maximum deviation and red suffering minimum deviation.
A lens can be assumed to be made up of a number of prisms.
The refracting angle of the prism goes on decreasing at a uniform rate from its centre outwards to its periphery. When white light is passed through a lens it is dispersed into its constituent colours.
The deviation is different for different colours and hence they come to focus at different points on the principal axis. Due to this we get a coloured and blurred image. This defect is called chromatic aberration.
Given,
f1 = 30 cm, w1 = 0.03
f2 = 20 cm, w2 = ?
Focal length of the combination,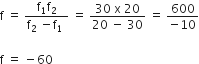
We know, 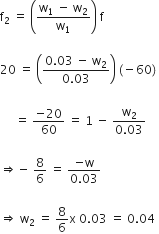
Electrons, initially at rest, are passed through a potential difference of 2 kV. Calculate their:
(i) Final velocity and
(ii) de Broglie wavelength.
