 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsArrange the following in the order of increasing mass (atomic mass O = 16, Cu = 63, N = 14)
I. One atom of oxygen
II. One atom of nitrogen
III. 1 × 10-10 mole of oxygen
IV. 1 × 10-10 mole of copper
II < I < III < IV
I < II < III < IV
III < II < IV < I
II < IV < I < III
Which transition in the hydrogen atomic spectrum will have the same wavelength as the transition will have the same wavelength, n = 4 to n = 2 of He+ spectrum?
n = 4 to n = 3
n = 2 to n = 1
n = 4 to n = 2
n = 3 to n = 1
Which of the following is not correct with respect to bond length of the species?
C2 >
> B2
> Li2
O2 > O
A mixture of ethane and ethene occupies 41 L at 1 atm and 500 K. The mixture reacts completely with mole of O2 to produce CO2 and H2O. The mole fraction of ethane and ethene in the mixture are respectively (R = 0.082 L atm K-1 mol-1)
0.50, 0.50
0.75, 0.25
0.67, 0.33
0.25, 0.75
The correct decreasing order of first ionisation enthalpies of five elements of the second period is
Be > B > C > N > F
N > F > C > B > Be
F > N > C > Be > B
N > F > B > C > Be
In the reaction H2S+ H2O2 → S+ 2H2O
H2S is an acid and H2O2 is a base
H2S is a base and H2O2 is an acid
H2S is an oxidising agent and H2O2 is a reducing agent
H2S is an reducing agent and H2O2 is a oxidising agent
D.
H2S is an reducing agent and H2O2 is a oxidising agent
Here, the oxidation number of S increases from -2 in H2S to 0 in elemental sulphur, while that of O decreases from -1 in H2O2 to -2 in H2O. Therefore, H2S is a reducing agent and H2O2 is an oxidising agent.
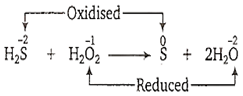
The bonds present in the structure of dichromate ion are
four equivalent Cr-O bonds only
six equivalent Cr-O bonds and one Cr - O - O bond
six equivalent Cr-O bonds and one O-O bond
eight equivalent Cr-O bonds
Molar heat capacity of aluminium is 25 JK-1 mol-1. The heat necessary to raise the temperature of 54 g of aluminium (atomic mass 27 g mol-1) from 30°C to 50°C is
1.5 kJ
0.5 kJ
1.0 kJ
2.5 kJ
