 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn a competition A, B, C are participating the probability that A wins is twice that of B, the probability that B wins is twice that of C, then probability that A loses is
The probability that a number selected at random from the set of numbers (1, 2, 3, ... , 100) is a cube, is
Two dice are rolled simultaneously. The probability that the sum of the two numbers on the dice is a prime number, is
0.25
The events A andB have probabilities 0.25 and 0.50, respectively. The probability that both A and B occur simultaneously is 0.14, then the probability that neither A nor B occurs, is
0.39
0.29
0.11
0.25
For all values of a and b the line (a + 2b)x + (a - by + (a + 5b) = 0 passes through the point.
(- 1, 2)
(2, - 1)
(- 2, 1)
(1, - 2)
The lines 2x + 3y = 6 , 2x + 3y = 8 cut the X-axis at A and B, respectively. A line L drawn through the point (2, 2) meets the X-axis as C in such away that abscissae of A, B and C are in arithmetic progression. Then, the equation of the line L is
2x + 3y = 10
8x + 2y = 10
2x - 3y = 10
8x - 2y = 10
The number of circles that touch all the straight lines x + y = 4,x - y = - 2 and y = 2 is
1
2
3
4
The orthocentre of triangle formed by the lines x + 3y = 10 and 6x2 + xy - y2 = 0 is
(1, 3)
(3, 1)
(- 1, 3)
(1, - 3)
A.
(1, 3)
The given lines are
x + 3y = 10 ...(i)
and 6x2 + xy - y2 = 0
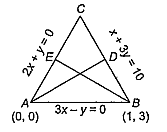
or 6x2 + 3xy - 2xy - y2 = 0
or 3x(2x + y) - y(2x + y) = 0
3x - y = 0 ...(ii)
2x + y = 0 ...(iii)
On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
If one of the lines of pair of straight lines ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 bisects the angle between the coordinate axes, then
a2 + b2 = h2
(a + b)2 = 4h2
a2 + b2 = 4h2
(a + b)2 = h2
