 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsLet PQRS be a quadrilateral. If M and N are the mid-points of the sides PQ and RS respectively, then PS + QR =
3 MN
4 MN
2 MN
2 NM
If vector r with dc's l, m, n is equally inclined to the coordinate axes, then the total number of such vectors is
4
6
8
2
At random variable X B(n, p), if values of mean and variance of X are 18 and 12 respectively, then total number of possible values of X are
54
55
12
18
The area of the region bounded by the lines y = 2x + 1, y = 3x + 1and x = 4 is
16 sq unit
8 sq unit
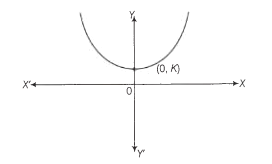
The differential equation of all parabolas whose axis is Y-axis, is
A.
The objective function of LPP defined over the convex set attains it optimum value at
atleast two of the corner points
all the corner points
atleast one of the corner points
None of the corner points
The equation of the plane through (- 1, 1, 2) whose normal makes equal acute angles with coordinate axes is
