 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of 30° with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is 0.8. If the frictional force on the block is 10 N, the mass of the block (in kg) is (take g = 10 m/s2 )
2.0
4.0
1.6
1.6
A force  is applied over a particle which displaces it from its origin to the
is applied over a particle which displaces it from its origin to the  .The work done on the particle in joules is
.The work done on the particle in joules is
-7
+7
+10
+10
A body of mass m accelerates uniformly from rest to v1 in time t1. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function of time t is




B.

Let the constant acceleration of body of mass m is a.
From equation of motion
v1 = 0 + at1
⇒ a = t2/t1 = ...... (i)
At an instant t, the velocity v of the body v = 0 + at
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle, the motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that
its velocity is constant
its acceleration is constant
its kinetic energy is constant
its kinetic energy is constant
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased keeping mass same which one of the following will not be affected?
moment of inertia
angular momentum
angular velocity
angular velocity
A ball is thrown from a point with a speed ν0 at an angle of projection θ. From the same point and at the same instant person starts running with a constant speed ν0/2 to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection?
yes, 60°
yes, 30°
no
no
A satellite of mass m revolves around the earth of radius R at a height x from its surface. If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth, the orbital speed of the satellite is
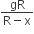
gx
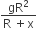
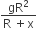
The time period of an earth satellite in circular orbit is independent of
the mass of the satellite
radius of its orbit
both the mass and radius of the orbit
both the mass and radius of the orbit
If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface, the gain in the potential energy of object of mass m raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to the radius R of the earth is
2 mgR
mgR/2
mgR/4
mgR/4
Suppose the gravitational force varies inversely as the nth power of distance. Then the time period planet in circular orbit of radius R around the sun will be proportional to


Rn
Rn
