 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFor which one of the following input combinations, the given logic circuit gives the output Y = 1 ?
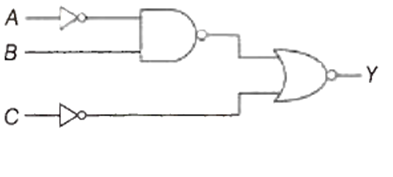
A = 0, B = 0, C = 0
A = 0, B = 1, C = 0
A = 0 ,B = 1, C = 1
A = 1 ,B = 1 ,C = 1
In a semiconductor, 2/3rd of the total current is carried by electrons and remaining 1/3rd by the holes. If at this temperature, the drift velocity of electrons is 3 times that of holes, the ratio of number density of electrons to that of holes is
In an p-n-p transistor, 1010 holes enter the emitter in 10-6 s. If 29% of holes is lost in the base, then the current amplification factor is
49
19
29
39
The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases when electromagnetic radiation of wavelength shorter than 600 nm is incident on it. The energy band gap (in eV) for the semiconductor is
1.50
0.75
2.06
1.35
Identify the mismatched pair
Noise — Unwanted signals
Repeater — Communication satellite
Attenuation — Srengthening of signal
Demodulation — Retrieval of information
Pick out the wrong statement.
Analog signals provide a continuous set of values
Digital signals represent values as discrete steps
Analog signals utilise the binary system
Digital signals can be processed by logic gates
A ground receiver receives a signal at 5 MHz, transmitted by a ground transmitter at a height of 320 m, which is 110 km away from it. Then it can communicate through (radius of the Earth, R = 6400 km)
space waves
ground waves
sky waves
both sky and ground waves
The power radiated by a linear antenna of length l at wavelength λ is
directly proportional to l
inversely proportional to λ
inversely proportional to λ2
directly proportional to λ2
C.
inversely proportional to λ2
The power radiated by a linear antenna of length l at wavelength λ is inversely proportional to λ2 i.e.
An aperture of size a is illuminated by a parallel beam of light of wavelength λ. The distance at which ray optics has a good approximation is
Two plane wavefronts of light, one incident on a thin convex lens and another on the refracting face of a thin prism. After refraction at them, the emerging wavefronts respectively become
plane wavefront and plane wavefront
plane wavefront and spherical wavefront
spherical wavefront and plane wavefront
spherical wavefront and spherical wavefront
