 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo convex lenses of same focal lengths but of aperture A1 and A2 (A2 < A1), are used as the objective lenses in two astronomical telescopes having identical eye-pieces. The ratio of their resolving powers is
1 : 1
data insufficient
A beam of light converges at a point P. A concave lens of focal length 16 cm is placed in the path of this beam 12 cm from P. The location of the point, from the lens, at which the beam would now converge is
48 cm
45 cm
80 cm
90 cm
A nucleus undergoes β-decay. The mass number and atomic number change as
mass number and atomic number both increases
mass number remain same and atomic number increases
mass number increases and atomic number remain same
mass number and atomic number both decreases
The graph given below showing the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of incident radiation for two different photosensitive materials having work functions W1 and W2 ( W1 < W2 ).

The slope of graph showing the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of incident radiation gives the value of
h/e where, h is Planck's constant and e electronic charge
h i.e, Planck's constant
e i.e, electronic charge
None of the above
A.
h/e where, h is Planck's constant and e electronic charge
The slope of graph showing the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of incident radiation gives the value of h/e, where h is Planck's constant and e is electronic charge whereas intercept of the lines gives the ratio of work function W and depend electronic charge e i.e. W/e.
In Young's double slit experiment, monochromatic light of wavelength 600 nm illuminates the pair of slits and produces an interference pattern in which two consecutive bright fringes are separated by 10 mm. Another source of monochromatic light produces the interference pattern in which of the two consecutive bright fringes are separated by 8 mm. The wavelength of light from the second source is
448 nm
450 nm
480 nm
580 nm
Light passes through two polaroids P1 and P2 with pass axis of P2 making an angle θ with the pass axis of P1. That value of θ for which the intensity of emergent light is zero.
45°
90°
30°
60°
If the angle between the axis of polarizer and the analyser is 45 degree, the ratio of the intensities of original light and the transmitted light after passing through the analyser is
2 : 1
1 : 2
2 : 3
1 : 1
A full wave rectifier circuit along with the output is shown in the figure. The contribution (s) from the diode 1 is ( are )
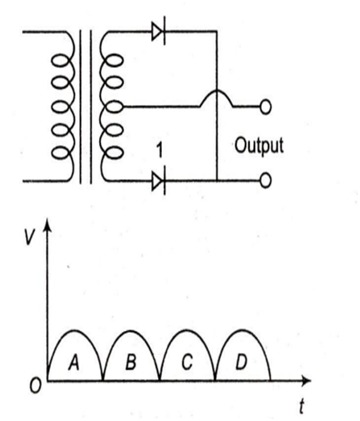
C
A , C
B , D
A, B , C , D
Two identical p-n junctions may be connected in series with a battery in three ways as shown in the figure.
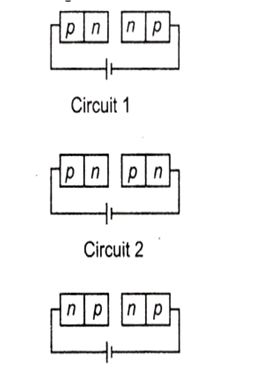
The potential drops across the two n-p junctions are equal in
circuit 1 and circuit 2
circuit 2 and circuit 3
circuit 3 and circuit 1
circuit 1 only
A transistor is used in common emitter mode as an amplifier, then
the base emitter junction is forward unbiased
the base emitter junction is reverse biased
the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to bias of the base emitter junction
the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to bias the emitter collector junction
