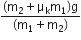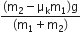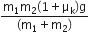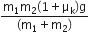Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIf energy (E), velocity (v) and time (T) are chosen as the fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be
[Ev-2T-1]
[Ev-1T-2]
[Ev-2T-2]
[Ev-2T-2]
A particle of unit mass undergoes one-dimensional motion such that its velocity according to
V(x) = βx-2n where β and n are constants and x is the position of the particle. The acceleration of the particle as a function of x is given by
-2nβ2 x-2n-1
-2nβ2 x-4n-1
-2β x-2n+1
-2β x-2n+1
Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants KP and KQ, such that KP>KQ. They are stretched, first by the same amount (case a), then by the same force (case b). The work done by the springs WP and WQ are related as, in case (a) and case (b), respectively
WP =WQ ;WP> WQ
WP =WQ ;WP= WQ
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
A block of mass 10 kg, moving in the x-direction with a constant speed of 10 ms-1 , is subjected to a retarding force F= 0.1x J/m during its travel from x = 20 m to 30 m. Its final KE will be
475 J
450 J
275 J
275 J
A particle of mass m is driven by a machine that delivers a constant power K watts. If the particle starts from rest, the force on the particle at time t is
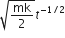



Two particles of masses m1,m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2. On collision, one of the particles gets excited to a higher level, after absorbing energy (E). If final velocities of particles be v1 and v2, then we must have




Kepler's third law states that square of the period of revolution (T) of a planet around the sun, is proportional to the third power of average distance r between the sun and planet i.e, T2 =Kr3, here K is constant.
If the masses of the sun and planet are M and m respectively, them as per Newton's law of gravitation force of attraction between them is 
The relation between G and K is described as
GK =4π2
GMK =4π2
K=G
K=G
A ship A is moving Westwards with a speed of 10 kmh-1 and a ship B 100km south of A, is moving Northwards with a speed of 10 kmh-1. The time after which the distance between them becomes shortest is
0 h
5 h


Three blocks A, B, and C of masses 4 kg, 2 kg and 1 kg respectively, are in contact on a 14 N is applied to the 4 kg block, then the contact force between A and B is
2 N
6 N
8 N
8 N
A block A of mass m1 rests on a horizontal table. A light string connected to it passes over a frictionless pulley at the edge of the table and from its other end, another block B of mass m2 is suspended. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is  . When the block A is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is
. When the block A is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is