Different products are formed depending upon the nature of the oxidising agent.
(i) Using alkaline potassium permanganate solution (Baeyer’s reagent): Alkenes react with a cold dilute alkaline solution of KMnO4 to produce diols.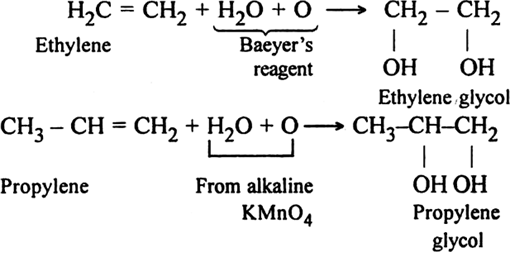
The pink colour of KMnO4 gets discharged and this reaction is known as Bayer's test for the detection of unsaturation in a compound.
(ii) Using hot KMnO4: Different products are formed depending upon the structure of alkene. In such reactions, the cleavage of C = C bond occurs.
In terminal alkenes: One of the product is always methanoic acid which is further oxidised to form CO2 and H2O.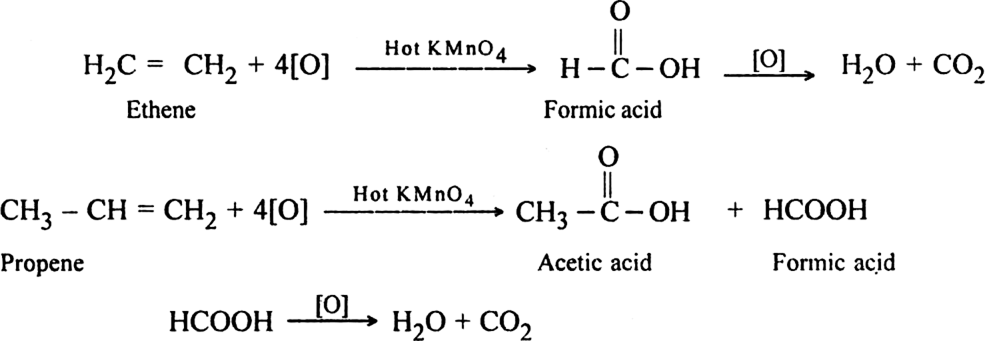
Note:= CH2 gets oxidised to CO2 and H2O.
In non-terminal alkenes. The products are carboxylic acids and/or ketones depending upon the nature of alkene.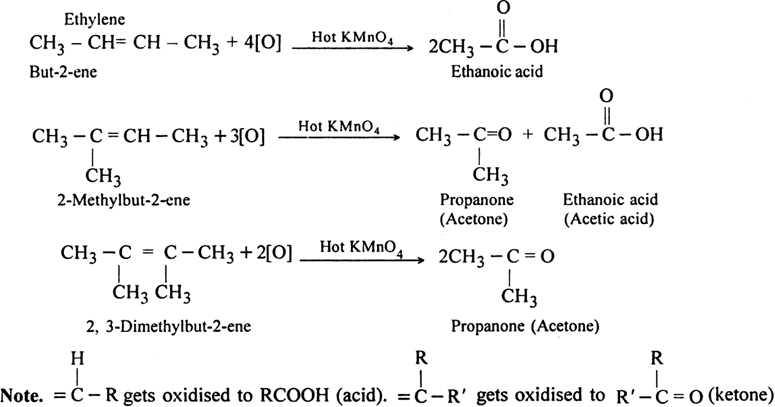
(iii) Using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Alkenes react with hydrogen peroxide to form diols.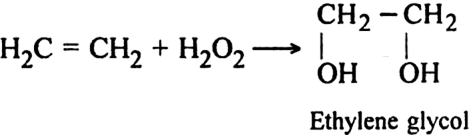
(iv) Using air in the presence of silver as a catalyst at 525-675 K. Ethylene forms ethylene oxide.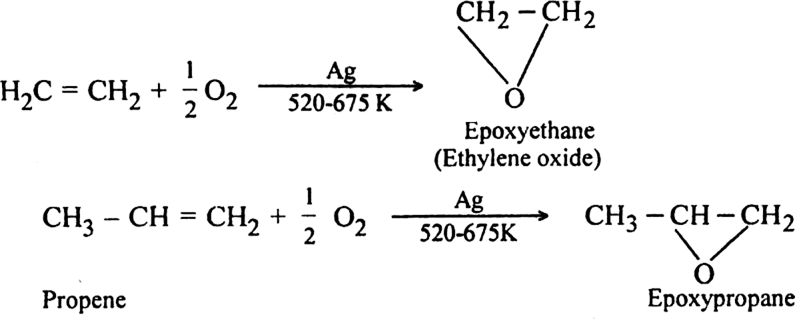
(v) Combustion. When burnt in air or oxygen, alkenes form carbon dioxide and water.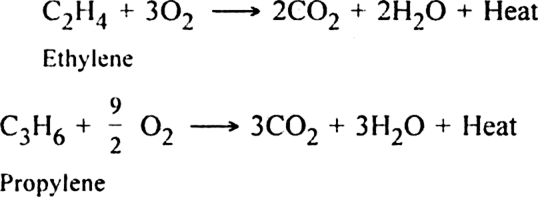
The reaction is highly exothermic in nature and the heat evolved is used for welding purposes.
