Catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes: It involves two types of hydrogenation.
(i) Complete hydrogenation: When vapours of alkynes are passed over the surface of the catalyst like Ni, Pt or Pd at 473 K, hydrogenation takes place to form alkenes and then alkanes. For example,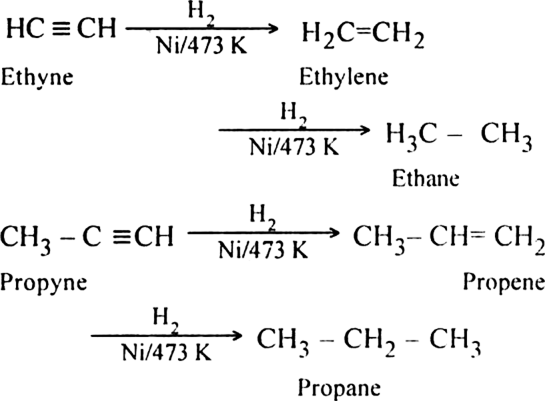
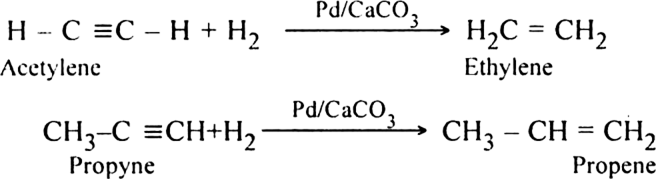
(ii) Controlled hydrogenation. When vapours of alkynes are passed over the heated Lindlar’s catalyst (Pd/CaCO3) partially poisoned by lead acetate or nickel boride catalyst known as P-2), controlled hydrogenation takes place only up to alkene stage.