Discuss the halogenation reactions of arenes.
Halogenation: Benzene reacts with chlorine or bromine in the presence of ferric or aluminium halide at room temperature to form substituted product. 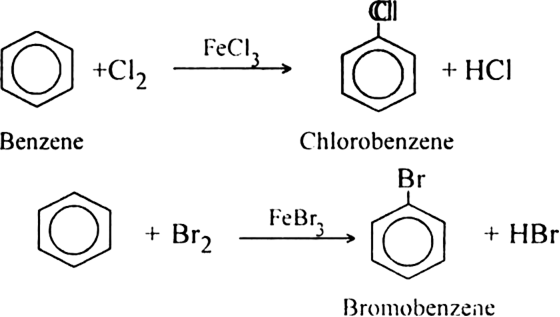
Iodination: Reaction of benzene with iodine is not possible because of its reversible nature i.e. HI formed reduces the iodo derivative back to the starting hydrocarbon.
However, the forward reaction is carried out by heating benzene with iodine in the presence of iodic acid (HIO3) which oxidises HI formed to iodine.
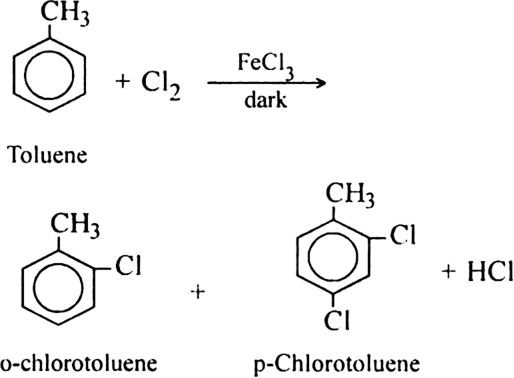
Similarly, toluene also undergoes halogenation under similar conditions giving a mixture of ortho and para disubstituted products.