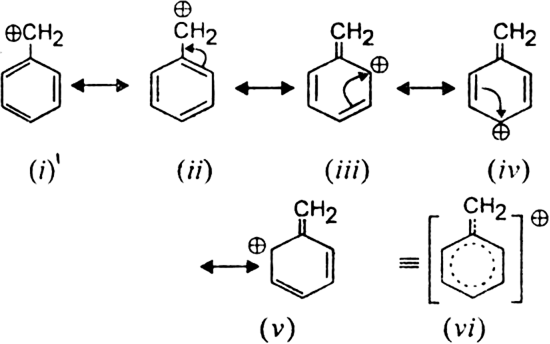
What is resonance? On its basis, explain the stability of benzyl carbocation.
Resonance may be defined as a phenomenon in which a single compound is supposed to be existing as a hybrid of two or more structures differing in the distribution of electrons and not of atoms. These different structures of a molecule are known as contributing structures or resonating structures or canonical forms. No one of the contributing structure truly represents the molecule, but each one of them contributes to the final i.e. actual structure is intermediate between all the contributing structures. Resonance effect is a process of permanent displacement of electrons in a molecule brought about by resonance. Resonance effect is transmitted through  ;-electrons and operates in unsaturated systems particularly those containing a suitable atom or group in conjugation with the unsaturated system. The stability of benzyl carbocation can be explained by a resonance effect. Benzyl carbocation is a resonance hybrid of the following contributing structures:
;-electrons and operates in unsaturated systems particularly those containing a suitable atom or group in conjugation with the unsaturated system. The stability of benzyl carbocation can be explained by a resonance effect. Benzyl carbocation is a resonance hybrid of the following contributing structures: