Account for the following:
(i) Chloroacetic acid has higher pKa value than acetic acid.
(ii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
i) Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid and has a higher value of dissociation constant Ka than that of acetic acid. We know that pKa= -log Ka, it means that chloroacetic acid having higher value Ka will have lower value of pKa, chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid because Cl group is electron withdrawing and chloroacetate ion is more stabilised than acetate ion.![]()
ii) Carboxyl group (-COOH) is electron withdrawing i.e deactivating the benzene ring and thus electron density becomes very less at ortho and para position in comparison to meta position. Electrophiles (+vely charged species) find it easier to attack at meta position as there is higher electron density this-COOH group is meta directing.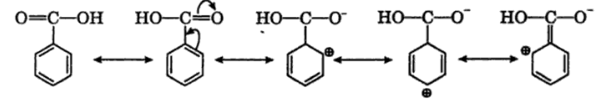
as there is a positive charge on ortho and para position, the electron density is higher at meta position and hence electrophilic substitution takes place at meta position.
iii) Carboxylic group (-COOH ) in acid is highly polar and generally, exist as dimers containing two hydrogen bond each as shown below:
These hydrogen bonds in carboxylic acid are stronger than those in alcohols. It is due to following two factors
a) the O-H bond of the carboxylic acids are more strongly polarised due to the adjacent electron-attracting >C=O groups.
b) the oxygen atom of the group >C=O in carboxylic acid is more negative as compared to the oxygen atom of the alcohol.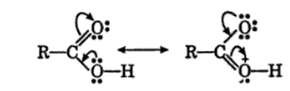
Thus carboxylic acids possesses higher boiling point than corresponding alcohols of similar molecular masses.
