Refraction of light: The phenomenon of bending of light from its straight line path as it passes obliquely from one transparent medium to another is called refraction of light.
The path of the ray of light in the first medium is called incident ray.
The path of the ray of light in the second medium is called refracted ray.
The angle between the incident ray and the normal at the surface of separation is called angle of incidence (i).
The angle between the refracted ray and the normal at the surface of separation is called angle of refraction (r).
Whenever a ray of light passes from one medium another, the following three situations are possible: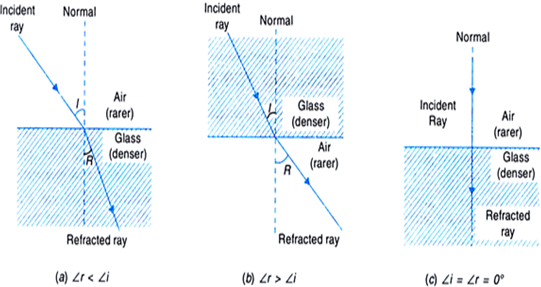
Fig.Refraction of light
(i) When a ray of light passes from an optically rarer medium to a denser medium, it bends towards the normal and ∠r < ∠i, as shown in Fig.(a).
(ii) When a ray of light passes from an optically denser to a rarer medium, it bends away form the normal and Lr > ∠i as shown in Fig.(b).
(iii) A ray of light travelling along the normal passes undeflected. Here ∠ i = ∠ r = 0°.
Some examples of refraction of light:
(i) When a pencil is partly immersed in water in a glass tumbler, it appears to be displaced at the interface of air and water. As shown in Fig(a) rays starting from point A in the optically denser medium bend away from normal after passing through water-air interface. On entering the eye, the ray appears to come from A'. Point A appears to be at A' and the portion AO appears to be at OA'. Thus the light reaching our eye from the portion of the pencil inside water appears to come from different direction, compared to the part above water. That is why the pencil appears bent at the interface.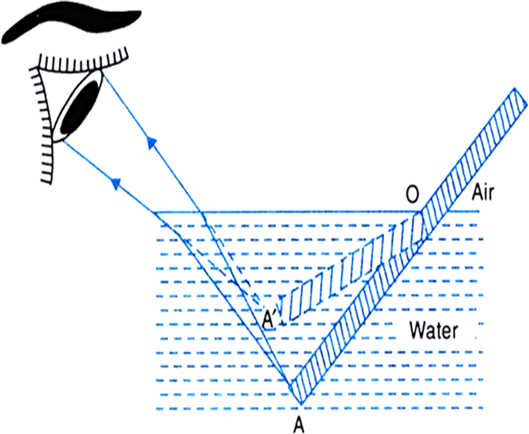
Fig.(a). A straight pencil partially put in water appears bent
If instead of water, we use liquids like kerosene or tarpentine, the pencil will appear to be displaced or bent by a different extent.
(ii) If we see a water tank, its botton appears to be raised. It also appears to be concave shaped although it is flat. Rays from A (Fig.(b)) after striking water-air interface bend away from normal. Thus point A appears to be at A' i.e., the bottom appears to be raised and concave.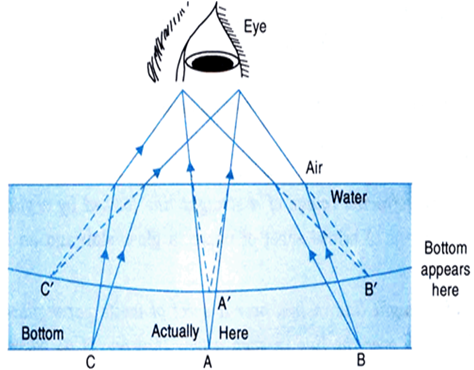
Fig.(b) The bottom of tank of water appears raised and concave shaped
For the same reason, when a thick glass slab is placed over some printed matter, its letters appear raised when seen through the slab.
