With the help of ray diagrams, explain the formation of images by a concave lens for the following positions of the object:
(i) Object at infinity
(ii) Object between infinity and optical centre O of the lens.
Image formation by a concave lens:
(i) Object at infinity: The rays from an object at infinity are parallel to each other. The rays diverge on refraction through the lens. A virtual, erect and extremely diminished image is formed at the focus F.
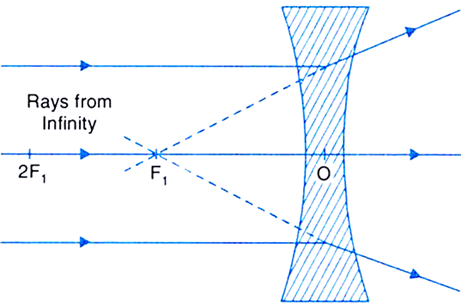 Fig. Image formed by a concave lens when the object is at infinity
Fig. Image formed by a concave lens when the object is at infinity
(ii) Object between infinity and optical centre O of the lens: A ray AN parallel to the principal axis, after refraction, appears to come from the focus F1. Another ray from lies between optical centre and infinity.
A passes undeviated through the optical centre O. The two rays appear to diverge from the point A'. Thus A' is the virtual image of A. Hence A'B' is the complete, virtual, erect and diminished image of the object AB. For all positions of the object the image is always virtual, erect and diminished and is formed between focus F
1 and the optical centre O.
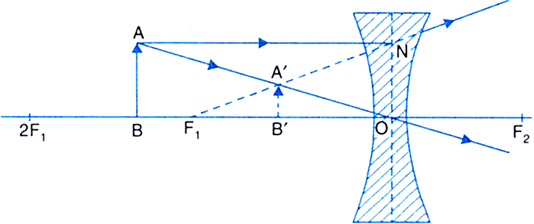
Fig. Image formed by a concave lens when the object
748 Views


