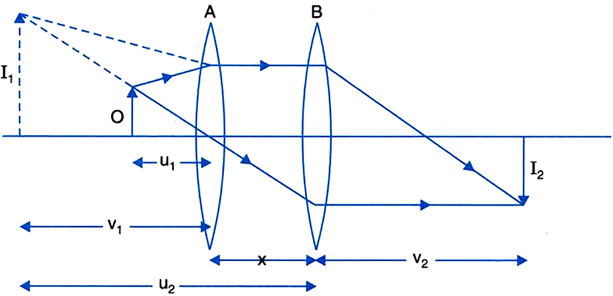
Two convex lenses A and B of focal lengths 20 cm and 10 cm are placed coaxially 10 cm apart. An object is placed on the common axis at a distance of 10 cm from lens A. Find the position and magnification of the final image.
From figure below, we have, for lens A
f1 = + 20 cm and u1 = –10 cm
The image distance v1 is given by
which gives 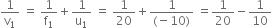

Thus, a virtual image is formed at I1 at a distance of 20 cm from lens A, if the lens B were absent. This image acts as a virtual object for lens B which forms the final image at I2 at a distance v2 from lens B.
For lens B we have,
x = 10 cm, u
2 = – (20 + 10) = –30 cm f
2 = + 10 cm.
 The image distance v2 is given by
The image distance v2 is given by 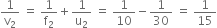
which gives
 Thus, a real image I2 is formed at a distance of 15 cm from lens B.
Thus, a real image I2 is formed at a distance of 15 cm from lens B.Magnification due to
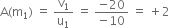
Magnification due to
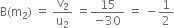
Magnification of the final image is
 This shows that the final image is inverted and is of the same size as the object.
This shows that the final image is inverted and is of the same size as the object.
341 Views

