State the principle of an ac generators and explain its working with the help of a labelled diagram. Obtain the expression for the emf induced in a coil havin N turns each of cross-sectional area, rotating with a constant angular speed 'ω' in a magnetic field , directed perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Principle − AC generator based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Construction:
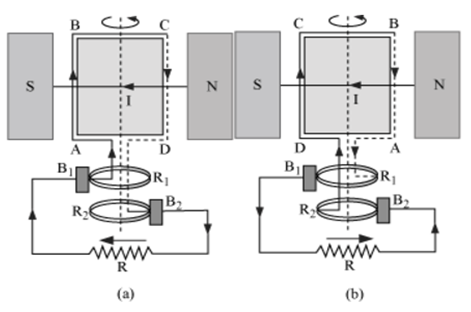
Main parts of an ac generator:
Armature − Rectangular coil ABCD
Filed Magnets − Two pole pieces of a strong electromagnet
Slip Rings − The ends of coil ABCD are connected to two hollow metallic rings R1 and R2.
Brushes − B1 and B2 are two flexible metal plates or carbon rods. They are fixed and are kept in tight contact with R1 and R2 respectively.
Theory and Working − As the armature coil is rotated in the magnetic field, angle θ between the field and normal to the coil changes continuously. Therefore, magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. An emf is induced in the coil. According to Fleming’s right-hand rule, current induced in AB is from A to B and it is from C to D in CD. In the external circuit, current flows from B2 to B1.
To calculate the magnitude of emf induced:
Suppose
A → Area of each turn of the coil
N → Number of turns in the coil
→ Strength of magnetic field
θ → Angle which normal to the coil makes with ![]() at any instant t
at any instant t
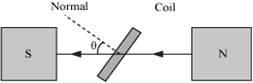
∴ Magnetic flux linked with the coil in this position:
= NBA cosθ= NBA cosωt …(i)
Where, ‘ω’ is angular velocity of the coil
As the coil rotates, angle θchanges. Therefore, magnetic flux Φ linked with the coil changes and hence, an emf is induced in the coil. At this instant t, if e is the emf induced in the coil, then

