
What is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand.
Spectro-chemical series is a series in which the ligands have been arranged in order of increasing magnitude of splitting they produce. The order is
I– < Br– < SCN– < Cl– < S2– < F – < OH– < C2O42– < H2O < NCS–< edta4– < NH3 < en < CN– < CO
The ligand present on the R.H.S of the series are strong field ligand while L.H.S are weak field ligand. Also, strong field ligand cause higher splitting in the d- orbitals than weak field ligand .
|
Weak field ligand |
Strong field ligand |
|
1.They are formed when the crystal field stabilisation energy (Δ0) in octahedral complexes is less than the energy required for an electron pairing in a single orbital (p).
|
1. They are formed when the crystal field stabilisation energy (Δ0) is greater than the p.
|
|
2. They are also called high spin complexes.
|
2. They are called low spin complexes.
|
|
3. They are mostly paramagnetic in nature complex.
|
3. They are mostly diamagnetic or less paramagnetic than weak field.
|
[Fe(CN)6]4 –
Outer electronic configuration of iron (Z = 26) in ground state is 3d64s2. Iron in this complex is in +2 oxidation state. Iron achieves +2 oxidation state by the loss of two 4s electrons. The resulting Fe2+ ion has outer electronic configuration of 3d6.
Since CN- is strong field ligand thus cause pairing.
It has been experimentally observed that this complex is diamagnetic as such has no unpaired electron. To account for this two unpaired electrons in the 3d - subshell pair up, thus leaving two 3d-orbitals empty. These two vacant 3d-orbitals along with one 4s-orbital and three 4p-orbitals hybridise to give six equivalent d2sp3 hybridised orbitals. Six pairs of electrons, one from each cyanide ion, occupy the six vacant hybrid orbitals so produced. The resulting complex ion has an octahedral geometry and is diamagnetic due to the absence of unpaired electrons.
The degenerate d-orbitals (in a spherical field environment) split into two levels i.e., eg and t2g in the presence of ligands. The splitting of the degenerate levels due to the presence of ligands is called the crystal-field splitting while the energy difference between the two levels (eg and t2g) is called the crystal-field splitting energy. It is denoted by ∆o.
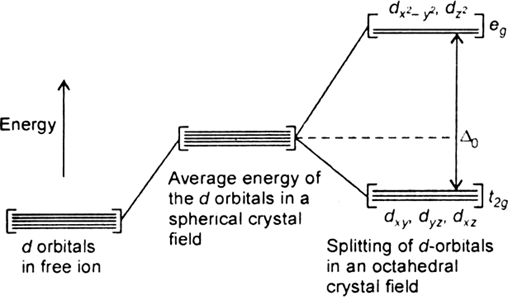
Fig. d-orbital splitting in an octahedral crystal field.
The formation of complex depend on the crystal field splitting, ∆o and pairing energy (P).
i)If ∆o < P, the fourth electron enters one of the eg orbitals giving theconfiguration t2g3. Ligands for which ∆o < P are known as weak field ligands and form high spin complexes.
ii) If ∆o > P, it becomes more energetically favourable for the fourth electron to occupy a t2g orbital with configuration t2g4 eg0. Ligands which produce this effect are known as strong field ligands and form low spin complexes.
Bonding in [FeF6]3–
The oxidation state of Fe is +3 and its coordination number is 6. The complex has octahedral geometry and experimental study shows that it is paramagnetic.
The bonding in this entity is explained on the basis of overlap of sp3d2 hybrid orbitals of Fe3+ ion and six lone pair orbitals of cyanide ligands. Five 3d electrons are unpaired which make it paramagnetic. The outer electronic configuration of Fe3+ ion is 3d5 which is highly stable and no pairing of electrons takes place in presence of weak field of F– ions. Here, 4d–orbitals of Fe3+ (which are empty) are involved.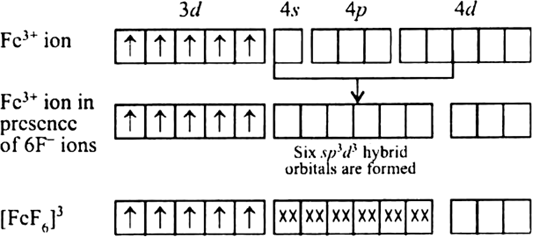
The entity is strongly paramagnetic due to five unpaired electrons and is an outer orbital complex.
Fluorine ion is a weak ligand. It cannot cause the pairing of the 3d electrons. As a result, the Co3+ ion will undergo sp3d2 hybridzation.
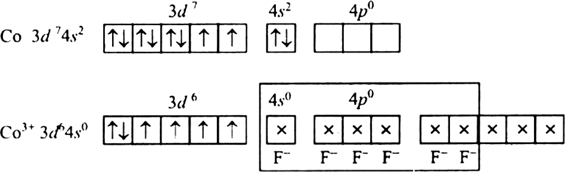
Hence, the geometry of the complex is octahedral and paramagnetic.
