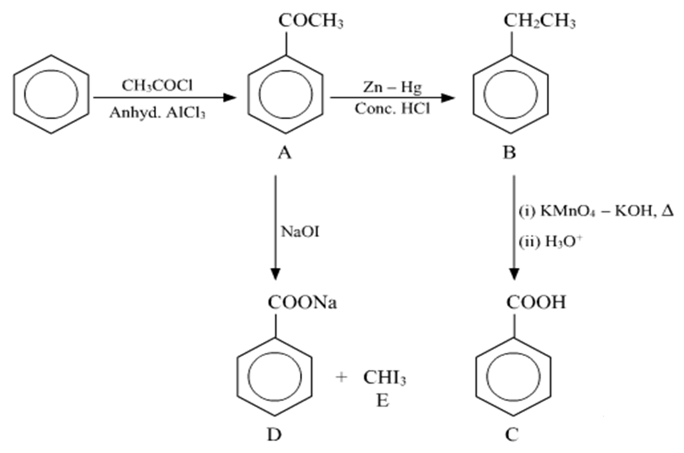
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions:
Or
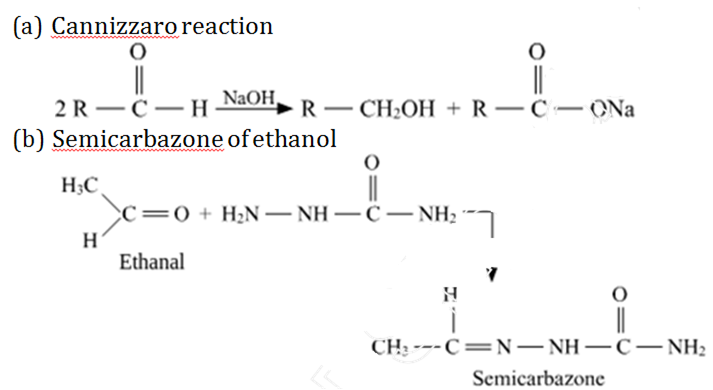
(a)Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in Cannizzaro reaction.
(b)Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(c)Why pKa of F-CH2-COOH is lower than that of Cl−CH2−COOH?
(d)Write the product in the following reaction: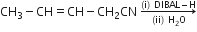
(e)How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone?

|
Propanal |
Propanone |
|
It forms silver mirror on reaction with Tollen's reagent. |
It is not oxidised by Tollen's reagent. |
|
It does not react with iodoform. |
It gives positive iodoform test. |
|
On reacting with Schiff's reagent, it gives pink colour. |
It does not react with Schiff's reagent. |
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
(b) How would you obtain the following?
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal
(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol
(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene
OR
(a) Given chemical tests to distinguish between the following:
(i) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following:
(i) Cannizaro reaction
In this reaction, the aldehydes which do not have a a-hydrogen atom, undergo self -oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with a concentrated alkali.
Example:
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
In this reaction, the carbonyl compounds are reduced in presence of zinc amalgam to give the corresponding alkane.
![]()
(b)
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal

(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol

(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene

Or
(a)
(i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate can be distinguished by sodium bicarbonate test.
Sodium bicarbonate test:
Acids react with NaHCO3 to produce brisk effervescence due to the evolution of CO2gas.Benzoic acid being an acid responds to this test, but ethyl benzoate does not.
![]()
(ii) Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) can be distinguished by iodoform test.
Acetophenone, being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH undergoes iodoform reaction to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform. On the other hand, benzaldehyde does not give this test.
b)

Distinguish between:
i) C6H5-COCH3 and C6H5-CHO
ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH
c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO,CH3COOH,CH3CH2OH
Or
a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff Kishner reduction.
b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
C6H5COCH3, CH3-CHO, CH3COCH3
c) why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group ?
d) Write the product in the following reaction![]()
e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomers B forms a yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.

(i)Heat both compounds with NaOH and I2, C6H5COCH3 forms yellow ppt of CHI3 whereas C6H5CHO does not.
(ii)Add ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent) to both the compounds, HCOOH gives silver mirror but CH3COOH does not.
C) CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
Or
a) ![]()
b)C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(c) Because of resonance in the carboxylic group the carbonyl group loses a double bond character.
d) ![]()
e) A : CH3CH2CHO B : CH3COCH3
(a) Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents:
(i) HCN
(ii) H2N−OH
(iii) CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol
(ii) Propanal and Propanone
OR
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Cl−CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of the carbonyl group.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Rosenmund reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro's reaction
(c) Out of CH3CH2−CO−CH2−CH3 and CH3CH2−CH2−CO−CH3, which gives iodoform test?
(i) Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) reacts with hydrogen cyanide HCN to give 2-Hydroxypropapanenitrile as product.

(ii) Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) reacts with Hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give acetaldoxime as a product.

(iii) The reaction of acetaldehyde with acetaldehyde in the presence of dilute NaOH, this is the kind of Aldol reaction by which obtained 3-hydroxybutanal as a product. Further, proceed reaction when using heat in the reaction, its gives aldol condensation product which is But-2-enal.

(b) Chemical tests to distinguish the following compounds:
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol : Benzoic acid and phenol can be distinguished by FeCl3 tests. Both reacts with FeCl3 to give different colours. Phenol reacts with FeCl3 to give violet coloured precipitate while benzoic acid gives buff coloured precipitate.
3C6H5OH +FeCl3 ---> (C6H5O)3Fe + 3HCl
phenol violet colour
3C6H5COOH +FeCl3 ---> (C6H5COO)3Fe +3HCl
Benzoic acid buff colour
(ii) Propanal and Propanone : These two are distinguished by the iodoform test.propanal does not give iodoform test when it reacts with I2 in the presence of NaOH while propanone give iodoform test when reacts with I2 in the presence of NaOH.
CH3COCH3 +3NaOI --> CHI3 + CH3COONa +2NaOH
Propane Yellow ppt
CH3CH2OH +NaOI ---> No ppt of CH3I formed
Or
a) (i) Cl-CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH :
Substitution of electron withdrawing group on carboxylic acid affect the acidity of the carboxylic acid. Chlorine is a electron withdrawing group and its increase the acidity of carboxylic acids by stabilising the conjugate base due to delocalisation of the negative charge by resonance effects.
Chloroacetic acid ( Cl-CH2COOH) pKa value is equal to 2.7, while pKa value of acetic acid (CH3COOH) is equal to 4.7.
(ii) In carboxylic acid presence of lone pairs of electrons on oxygen which are involves in resonance due to this the electrophilic character of carbon in carboxylic acid decreases. So due to such reason carboxylic acid does not show the characteristic reaction of the carbonyl group.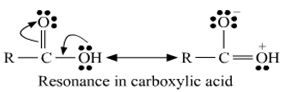
b)
i)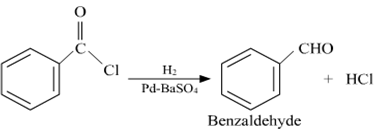
ii)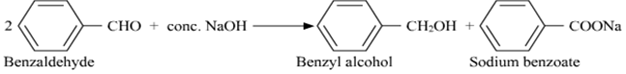
C )
Pentan-2-one (CH3-CH2-CH2-CO-CH3) give yellow precipitate of CHI3 with NaOI, that means it gives iodoform test.
CH3-CH2-CH2-CO-CH3 + 3NaOI --> CHI3 + CH3CH2COONa + 2NaOH
Yellow
ppt.
Pentan-3-one (CH3-CH2-CO-CH2-CH3) does not give yellow precipitate with CHI3 with NaOI, so Pentan-3-one does not give iodoform test.
i) Mn Shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4.
ii) Cr2+ is a strong reducing agent.
iii) Cu2+ salts are coloured while Zn2+ salts are white.
b) Complete the following equations:
i) Mn Shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine, it shows the highest oxidation state of +4 because of the ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds with Mn metal.
ii) Cr2+ is strongly reducing in nature. It has a d4 configuration. Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent because it can lose one of its electrons to become Cr3+ in which the t2g level of d-orbital is half filled and the eg level is empty which is a more stable configuration.
iii) The electronic configuration of Zn = 3d10 4s2
Zn2+ = 3d10
where as the electronic configuration of Cu = 3d10 4s1
Cu2+ =3d9
In the case of Zn fully filled d orbital is present therefore no d-d transition can be possible in this case and it is colourless.
In the case of copper 3d9 because of d-d transition electrons emits light in the visible range and hence they are coloured compounds.

