Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors
In India, a government agency, named, Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) which computes official estimates of national income and related aggregates has divided the entire economy into following three sectors. Broadly primary sector exploits natural resources; secondary sector transforms one type of commodity into other; and tertiary sector renders services as explained below.
(i) Primary sector (also called Agricultural sector). This sector includes all production units which produce goods by exploiting natural resources. These include resources like water, forests, agricultural land, coal, iron ore and other minerals, etc. Thus, this sector consists of man's primary occupations such as farming, fishing, mining, etc. This sector supplies basic raw material to secondary sector.
(ii) Secondary sector (also called Manufacturing sector). This sector includes all production units which are engaged in producing goods by transforming raw material (received from primary sector) into finished products or one type of commodity into another type of commodity. Examples are cloth mills, sugar mills, steel industry, shoe factory, biscuit factory, etc.
(iii) Tertiary sector (also called Service sector). This sector consists of producing units which are engaged in producing services. For example, banks, transport companies, insurance companies, educational and medical institutions, etc. Thus, tertiary sector provides useful services to the other two sectors.
Mind, expenditure method gives us the value of GDP at MP when measured at the point of expenditure. From expenditure point of view, GDP is gross expenditure on the final use of domestically produced goods and services during a period of account. Basically final use or disposition of goods and services is for two purposes : consumption purposes for direct satisfaction of wants and investment purposes for expanding productive capacity. And expenditure on them is called final consumption expenditure and final investment expenditure. They are further subdivided into five components as shown below. Total final expenditure is equal to GDP at MP. By subtracting depreciation and net indirect taxes from GDPMP, we get NDPFC (Domestic Product) and by adding to it net factor income from abroad to NDPFC, we get national product (NNPFC).
The following components of GDP are given to help solve numerical sums by expenditure method. Symbolically :
GDPMP = Private final consumption expenditure + Government final consumption expenditure + Gross fixed capital formation + Change in stocks + Net exports.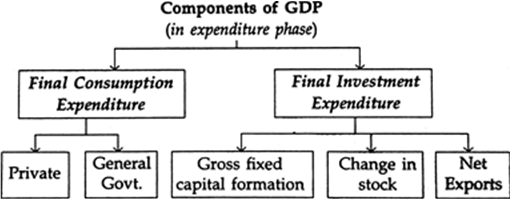
Let us discuss briefly each component and see how final expenditure on GDP is arrived at. Mind, final expenditure is that part of expenditure which is incurred on final use of goods and services and not for intermediate purpose.
1. Private final consumption expenditure. It measures the money value of goods and services purchased by households and non-profit institutions for current use during a time period. In this category we include consumption expenditure by consumer households and private non-profit institutions serving households on all types of consumer goods (i.e., durable, semi-durable, non-durable goods and services). Goods are tangible (which can be seen and touched) whereas services are intangible since they have no volume and shape. Private final consumption expenditure includes all categories of consumer goods and services.
2. Government final consumption expenditure. It is defined as "Current expenditure on goods and services incurred in providing services of government administrative departments less sales." It is incurred by general government to satisfy collective needs of the people. For example, Government expenditure on health, education, general administration, law and order, etc. belongs to this category.
3. Gross fixed capital formation. This refers to increase in stock of fixed capital during a year which includes depreciation. Expenditure on it consists of the following three main items.
(i) Business fixed investment. It is defined as addition to machinery, factory, building and equipment.
(ii) Residential construction investment. It refers to addition of housing facilities.
(iii) Public investment. It refers to capital formation by government in the form of schools, hospitals, roads, bridges, canals, etc.
4. Change in stocks. This refers to the physical change in stocks of inventories like raw material, semi-finished goods and finished goods lying with the producers for smooth working of production process. It is the difference between the stocks in the beginning and in the end of the year. Expenditure on it is found out by multiplying the physical change in stocks (lying with the producers) with the market prices. It should be noted that value of change in stock of goods lying with consumers should not be included because all consumer goods are deemed as consumed the moment they are purchased by consumers.
Note : According to SNA. 1993 'net acquisition of valuables' is also a part of gross domestic capital formation, and therefore, it should be treated as component of GDP in expenditure phase.
5, Net exports. (Exports less imports). This refers to the difference between value of exports (e.g., expenditure by foreigners on direct purchase of Indian products) and value of imports (i.e., expenditure by Indians on direct purchase of foreign goods). Be it noted that from expenditure point of view, value of exports is added and that of imports deducted. Mind, exports and imports include both material goods as well as services (non-factor services). Remember, when value of imports is greater than that of exports, it is called net imports. Again exports are treated as investment in foreign country by exporting country and imports as disinvestment. Thus net exports (exports less imports) indicate net investment abroad.
Is export a part of domestic product? Yes, because all the goods and services which are exported are produced by the producers in the domestic economy. For instance, Indian tea, coffee, jute goods, etc. which are purchased by foreigners are produced in India and it is called India's export. In short, since exported goods and services are produced in domestic territory of a country, therefore, export of goods and services is a part of gross domestic product (GDP). Mind export receipts are not 'net factor income from abroad' as they are revenue of the firms from sale of their products.
Components of GDP in expenditure phase are illustrated with the help of the following extract from statement-5 of Government of India publication NAS, 2007.
Consolidated Account of the Nation
Gross Domestic Product and Expenditure
(at current prices) (र in crores)
|
Item |
Year 2004-05 |
2005-06 |
|
|
(i) |
Govt. final consumption expenditure |
3,42,542 |
4,04,511 |
|
(ii) |
Private final consumption expenditure |
18,65,645 |
20,64,638 |
|
(iii) |
Gross fixed capital formation |
8,22,786 |
10,00,760 |
|
(iv) |
Change in stocks |
63,789 |
1,04,036 |
|
(v) |
(a) Export of goods and services |
5,69,051 |
7,25,124 |
|
(b) Less Imports of goods and services |
6,25,945 |
8,30,678 |
|
|
(vi) |
Discrepancies |
47,674 |
56,329 |
|
Expenditure on GDP |
31,26,596 |
35,67,177 |
Source : NAS, 2007 of Government of India.
How is equality of three methods
Reconcile three methods of measuring national income.

From the following data calculate national income, domestic income, personal income and personal disposable income :
|
(र) |
|
|
Rent |
5,000 |
|
Wages |
30,000 |
|
Interest |
8,000 |
|
Surplus of public sector |
15,000 |
|
Profit tax |
2,000 |
|
Personal tax |
1,500 |
|
Mixed income |
4,000 |
|
Undistributed profit |
3,000 |
|
Transfer payment by government |
1,000 |
|
Dividend |
12,000 |
|
Net assets income from abroad |
7,000 |
|
Transfer from abroad |
2,500 |
National Income = Rent + Wages + Interest + Mixed income + Profit tax + Dividend + Undistributed profit + Surplus of public sector + Net assets income from abroad.
= 5,000 + 30,000 + 8,000 + 4,000 + 2,000 + 12,000 + 3,000 + 15,000 + 7,000
= 86,000
Domestic Income = National income - Net assets income from abroad
= 86,000 - 7,000 = 79,000
Personal Income = National income - Profit tax - Undistributed profit - Surplus of public sector + Transfer payment by government + Transfers from abroad
= 86,000 - 2,000 - 3,000 - 15,000 + 1,000 + 2,500
= 69,500
Personal disposable income = Personal income - Personal tax
= 69,500 - 15,00 = 68,000
