Write structure, location and function of squamous epithelium, cuboidal epithelium, columnar epithelium and striated squamous.
| Type of tissue | Structure | Location in the body |
Function |
|
| 1. | Squamous epithelium | Cells are flat, discoi-dal and fit together forming a pavement like appearance. | Alveoli of the lungs Blood capillaries. Bowman’s capsule of nephron in kidney. |
Exchange of gases in the lungs. Exchange of materials and gases between body cells and blood. Ultrafiltration of blood. |
| 2. | Cuboidal epithelium | Cells are cuboidal with centric and rounded nuclei. |
Tubule of nephron in kidney. Duct of salivary glands. |
Selective reabsorption of useful materials and water. Production of gametes. |
| 3. | Columnar epithelium | Cells are more tall than wide, placed side by side. The nucleus is situated near the bases. |
Fallopian tube (ciliated cells). Mucosa of small intestine (cells with microvilli). |
Help in movement of ovum/zygote. Absorption of digested food with increased surface area. |
| 4. |
Striated squamous |
Squamous flat cells arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear of parts. |
Skin, tongue, oesophagus lining of mouth. |
Protection, prevent wear and tear. |
Explain the structure of three types of muscle fibres. Also write the locations where they are found in the body.
The following are the three types of muscle cells:
(i) Unstriped. (Also known as smooth, involuntary or plain muscles). This type of muscular tissue consists of spindle-shaped, long fibre-like cell with a nucleus at the centre. The ends are undivided. This type of muscles is present in alimentary canal, muscular coat of blood vessels etc.
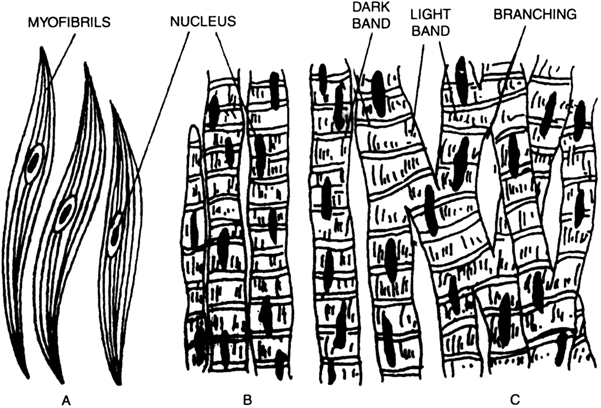
(ii) Striated muscles. (Also known as striped or voluntary muscles because of their function being in our control or will). This type of muscular tissue cells are very long fibres, enclosed in a membrane known as sarcolemma. The cells (fibre) are multi-nucleated. Each fibre has several longitudinal myofibrils embedded in cytoplasm. On these myofibrils are present characteristic light and dark bands which give it a striated appearance. These muscles are attached to the skeleton; so are also called skeletal muscles,
(iii) Cardiac muscles. These muscles are found in heart. They are not under the control of the will. They contract rhythmically and involuntarily throughout life without the sign of fatigue.
Structurally they show the characters of both unstriated and striated muscles. They are made up of branched fibres. These fibres are multinucleated and show alternate light and dark bands (striation).
What are the five main functions of simple epithelial tissues?
The main functions of simple epithelial tissues are:
(i) The cells form the outer layer of skin. They protect the underlying cells from drying, injury, infection and chemical effects.
(ii) They regulate the exchange of materials between the body and the external environment.
(iii) They help in absorption of water and other nutrients, especially in alimentary canal.
(iv) They help in the elimination of waste products.
(v) Some of them are greatly specialized (glandular cells) and perform secretory function.
What are epithelial tissues?
Epithelial Tissues is the tissue that forms a protective covering on an external or internal surfaces of the animals. The cells are tightly packed and form a continuos sheet. These tissue have no intercellular spaces and have small amount od cementing material between them. An epithelial tissue may be composed of one (simple epithelium) or more layers of cells (compound epithelium). The skin, surface layers of mouth, alimentary canal, lungs etc. are made of epithelial tissues. It also forms a barrier to keep different body system separate and also regulates the exchange of materials between the body and the external enviroment.
What are the various forms of cells of epithelial tissue? Describe briefly.
These cells form of the Simple epithelial tissue:
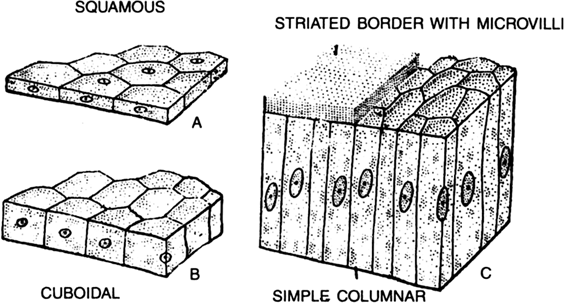
(i) Squamous epithelium. The cells of this tissue are broad, flat forming a pavement like appearance. It is found in the alveoli of the lungs. Bowman’s capsule, membranous labyrinth of internal ear, peritoneum of coelom and blood vessels.
(ii) Cuboidal epithelium. The cells of this tissue are cube like in appearance. It is found in kidney tubules and salivery glands etc.
(iii) Columnar epithelium. The cells of this tissue are more tall than wide, placed side by side. Their nuclei are situated near the bases. They may have on their free surfaces finger like projections—the microvilli. This tissue usually lines the internal surfaces of stomach and intestine.
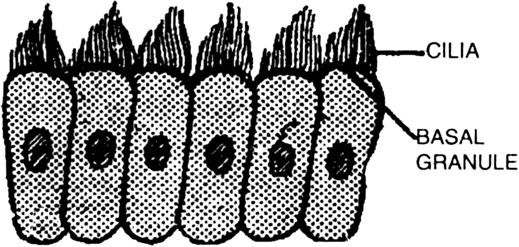

(iv) Ciliated epithelium. The cells of this tissue are modifications of columnar epithelial cells. They have on their free ends many small, vibratile cilia. These are found in kidney tubules, trachea oviduct etc.
(v) Striated squamous epithelium. Cells of this tissue are squamous epithelial cells which are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear of parts. Tounge, oesophagus and lining of mouth are also made of striated squamous epithelium.
(vi) Glandular epithelium. Sometimes the cells aggregate to form masses of cells, the glands. These glands secrete juices helpful to the organism. We have a number of such glands in our body, viz. sweat glands which secrete sweat; oil glands which secrete oily substance. Both these glands are present in the skin. Salivery glands present in the mouth secrete saliva.
(vii) Sensory epithelium. At certain places the cells of columnar epithelium gets modified into sensory cells. These cells are innervated at their bases by sensory nerve fibres. Such cells are found in sense organs.
(viii) Germinal epithelium. They are found in gonads i.e., testes and ovaries. They produces gametes i.e., sperms and ova.
