Angle of prism, A = 60o
Refractive index of prism = 1.5
Given, angle of incidence , i1=i2 = = = 45o
As, A + = i1 + i2
60o + = 45o + 45o
Then, angle of minimum deviation, = 90o - 60o = 30o
We know that, velocity of light in vacuum = 3108 m/s
Now, using the formula,
That is,
is the required speed of light in the prism.
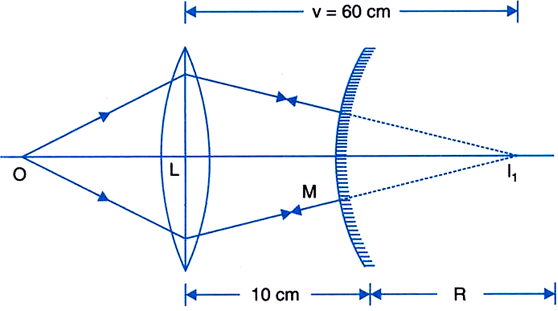
Thus, in the absence of the convex mirror, convex lens will form the image I1, at a distance of 60 cm behind the lens. As the mirror is at a distance of 10 cm from the lens, I1 will be at a distance of (60 – 10) = 50 cm from the mirror, i.e., MI1 = 50 cm.
Now, as the final image I2 is formed at the object itself, the rays after reflection from the mirror retraces its path, i.e., the rays on the mirror are incident normally, i.e., I1 is the centre of the mirror so that
![]()
and ![]()